Solutions to the Practice Problems#
But First, What is a Node?#
Node<Integer> node1 = new Node<>(100); Node<Integer> node2 = new Node<>(15); Node<Integer> node3 = new Node<>(150); Node<Integer> node4 = new Node<>(75);
node2.setNext(node4); node4.setNext(node1); node1.setNext(node3);
node2.getNext().getNext().getNext().getValue()
Use your own name, but here is a solution for “Rosanna”:
Node<Character> node1 = new Node<>('R'); Node<Character> node2 = new Node<>('o'); Node<Character> node3 = new Node<>('s'); Node<Character> node4 = new Node<>('a'); Node<Character> node5 = new Node<>('n'); Node<Character> node6 = new Node<>('n'); Node<Character> node7 = new Node<>('a'); node1.setNext(node2); node2.setNext(node3); node3.setNext(node4); node4.setNext(node5); node5.setNext(node6); node6.setNext(node7);
The Linked List Data Type#
public Node<V> getHead(){ return head; }
public Node<V> getTail(){ return tail; }
public int getSize(){ return size; }
Operations (Methods) for a Linked List#
LinkedList<String> favFoods = new LinkedList<>(); favFoods.addFirst("blueberries"); favFoods.addFirst("pizza"); favFoods.addFirst("fresh garden salad"); favFoods.addFirst("vanilla ice cream"); favFoods.addFirst("pepper steak"); System.out.println("My favorite foods are: " + favFoods);
public class CourseMark { private String course; private double mark; public CourseMark(String course, double mark){ this.course = course; this.mark = mark; } @Override public String toString(){ return course + " " + mark; } } //class CourseMark //In main, or somewhere else: LinkedList<CourseMark> myMarks = new LinkedList<>(); myMarks.addFirst(new CourseMark("AUCSC 112", 97)); myMarks.addFirst(new CourseMark("AUMAT 116", 85)); myMarks.addFirst(new CourseMark("AUMAT 120", 92)); myMarks.addFirst(new CourseMark("AUIDS 101", 78)); System.out.println("My courses and marks: " + myMarks);
/** * Finds the average of the integer values in a linked list. * * @param intList - Linked List made of Integers * @return - the average of the integers in the list. NOTE: if the * list is empty, returns 0. */ public static double findAvLL(LinkedList<Integer> intList){ Node<Integer> cursor = intList.getHead(); double sum = 0; if (cursor == null){ //nothing in list return 0; } while (cursor != null){ sum = sum + cursor.getValue(); cursor = cursor.getNext(); } return sum / intList.getSize(); }
/** * Add a node onto the end of the list, with node containing * the value given. * * @param aValue - value to put into the node to add */ public void addLast(V aValue){ Node<V> aNode = new Node<>(); aNode.setValue(aValue); if (size == 0){ head = aNode; } else{ tail.setNext(aNode); } tail = aNode; size++; }
/** * Adds a node into the linked list, the node has 1st value and * is inserted right after the node with the 2nd value. * * @param addValue - insert a node with this value * @param addAfterValue - right after a node with this value * NOTE: if the 2nd value is not in the linked list, nothing is * done but an error message is printed. */ public void addAfter(V addValue, V addAfterValue){ Node<V> location = findNode(addAfterValue); if (location == null){ System.out.println("ERROR - value " + addAfterValue + " not found"); } else{ Node<V> newNode = new Node<>(addValue); newNode.setNext(location.getNext()); location.setNext(newNode); if (tail == location){ //adding at the end tail = newNode; } } }
Other Kinds of Linked Lists#
public class DNode<V> { //Instance Fields =========================== private V value; private DNode<V> next; private DNode<V> previous; //Constructors ============================== public DNode(V inValue, DNode<V> toNode, DNode<V> fromNode) { value = inValue; next = toNode; previous = fromNode; } public DNode(V inValue) { this(inValue, null, null); } public DNode() { this(null, null, null); } //Getters ==================================== public V getValue() { return value; } public DNode<V> getNext() { return next; } public DNode<V> getPrevious() { return previous; } //Setters ===================================== public void setValue(V value) { this.value = value; } public void setNext(DNode<V> next) { this.next = next; } public void setPrevious(DNode<V> previous) { this.previous = previous; } }
/** * Adds a node with an element to the "front" of the list. * * @param value - the new information to store in the new node */ public void addFirst(V value) { if (size == 0) { //if list is empty, then this node is the only node entry = new Node<>(value); entry.setNext(entry); //circle on itself } else { //put node in at entry, list has at least 1 node already Node<V> newNode = new Node<>(value); newNode.setNext(entry.getNext()); entry.setNext(newNode); entry = newNode; } size++; }//addFirst
public void addLast(V aValue){ DNode<V> aNode = new DNode<>(); aNode.setValue(aValue); if (size == 0){ head = aNode; tail = aNode; } else{ aNode.setPrevious(tail); tail.setNext(aNode); } tail = aNode; size++; }
End of double: \(\theta(1)\)
End of single: \(\theta(1)\)\(\theta (n)\) as we would have to find the middle
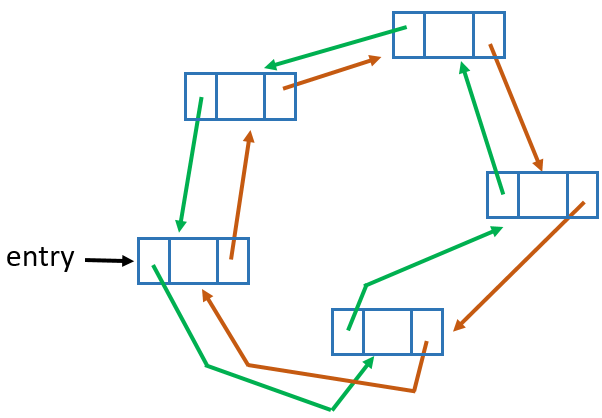
Advantage: can traverse easily in both directions.
Disadvantage: extra memory required for the 2nd link.