| (5.149) |
We now consider the improper Lorentz transformation of reflection in space or the parity transformation:
| (5.149) |
We need to solve (5.122) for
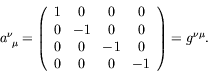 |
(5.150) |
We denote the Lorentz operator ![]() by
by ![]() for parity.
Consider the following ansatz
for parity.
Consider the following ansatz
| (5.151) |
where ![]() is an arbitrary phase.
Using equation 5.122, we have
is an arbitrary phase.
Using equation 5.122, we have
| (5.152) |
as required.
In analogy to the proper Lorentz transformation for which a rotation
of ![]() reproduces the original spinors, we postulate that four
space-inversions will reproduce the original spinors.
reproduces the original spinors, we postulate that four
space-inversions will reproduce the original spinors.
| (5.153) |
Therefore
| (5.154) |
We see that
| (5.155) | |||
| (5.156) |
and
![]() is unitary.
is unitary.
The wave function thus transforms as
| (5.157) |
In the nonrelativisitc limit ![]() approaches an eigenstate of
approaches an eigenstate of ![]() .
The positive- and negative-energy states at rest have opposite
eigenvalues, or intrinsic parities.
The intrinsic parity of a Dirac particle and antiparticle are opposite.
This is to be contrasted to the Klein-Gordon case wherein one finds
identical parities for the particle and antiparticle solutions.
.
The positive- and negative-energy states at rest have opposite
eigenvalues, or intrinsic parities.
The intrinsic parity of a Dirac particle and antiparticle are opposite.
This is to be contrasted to the Klein-Gordon case wherein one finds
identical parities for the particle and antiparticle solutions.