Geomagnetic Jerks
Geomagnetic jerks are sudden changes in the second time-derivative in the Earth's magnetic field observed at the surface. I co-authored a study showing that jerks can be explained by rigid zonal flows acting on the magnetic field at the top of the core. One important result of this study is that, while rigid zonal flows are global, whether a jerk occurs or not depends on the local morphology of the magnetic field (see Figure 1 below). While this captures some aspects of jerks, more recent work has shown that this only offers a partial explanation.
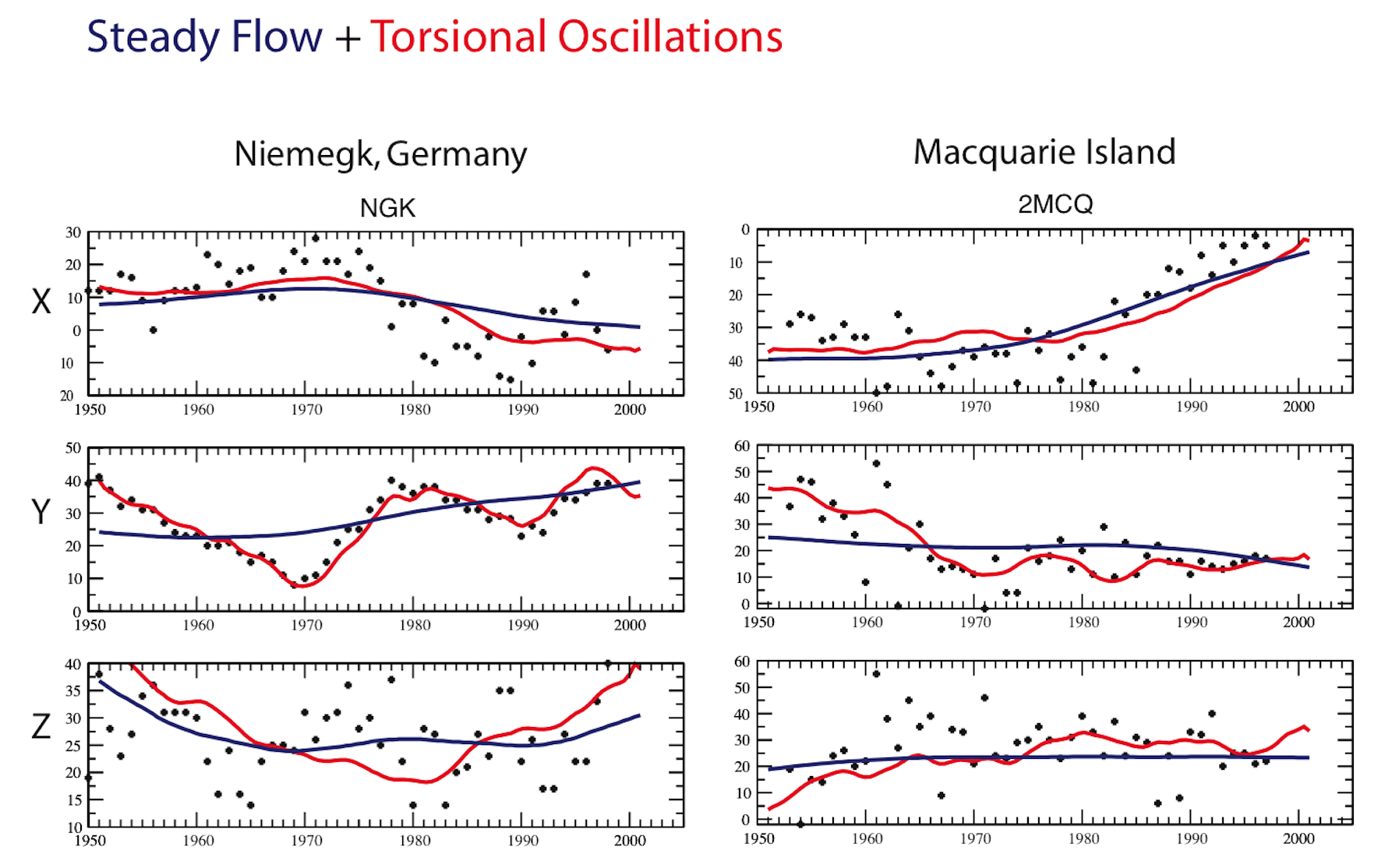 Figure 1: First time-derivative of the annual means of the
X, Y and Z components of the Earth's magnetic field (dots) at two
observatories at the Earth's surface: Niemegk (Germany) and Macquarie
Island (Pacific ocean). The sudden changes in the trend of the Y
component in Germany are geomagnetic jerks. The red curves are a prediction reconstructed
from a steady flow + rigid zonal motions only. Note that this
prediction can explain the jerks in Europe (though this is less
succesful in other places around the globe). Figure adapted from
Bloxham et al, Nature, 2002.
Figure 1: First time-derivative of the annual means of the
X, Y and Z components of the Earth's magnetic field (dots) at two
observatories at the Earth's surface: Niemegk (Germany) and Macquarie
Island (Pacific ocean). The sudden changes in the trend of the Y
component in Germany are geomagnetic jerks. The red curves are a prediction reconstructed
from a steady flow + rigid zonal motions only. Note that this
prediction can explain the jerks in Europe (though this is less
succesful in other places around the globe). Figure adapted from
Bloxham et al, Nature, 2002.
|
Paper on this topic
Bloxham, J., Zatman, S. and Dumberry, M., 2002, The origin of geomagnetic jerks, Nature, 420, 65-68.

