Frontline battle against COVID-19 inspires innovative respirator project
Feb 1, 2020
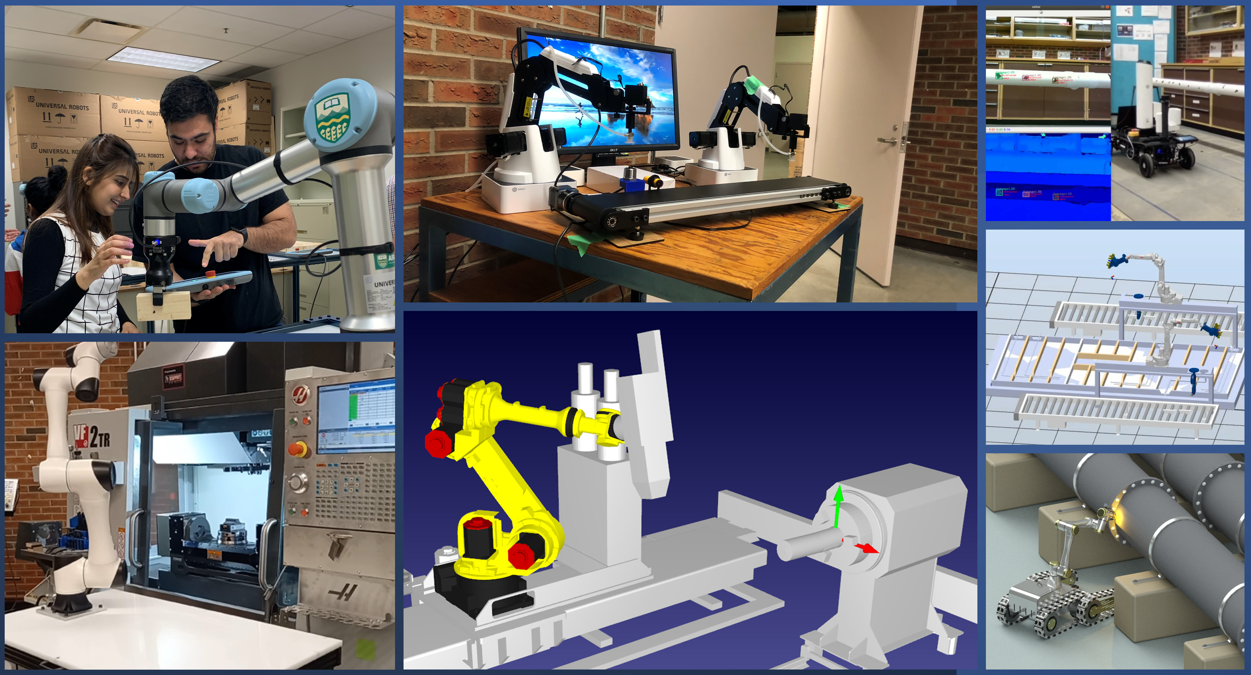

This research project aims to adopt robotics and digital twin technologies to various manufacturing processes, including repair, remanufacturing, recycling, inspection, pick-n-place, construction, and vertical farming. It supports the use of artificial intelligence techniques to improve productivity and automation. The digital twin models developed are based on IoT technology, databases, centralized control of the system, and a virtual interface that gives users full control and visualizes the state of the manufacturing system in real-time.

We provide complete process piping capabilities for industrial from paper. Laboratories used for scientific research take many forms because of the differing requirements of specialists.
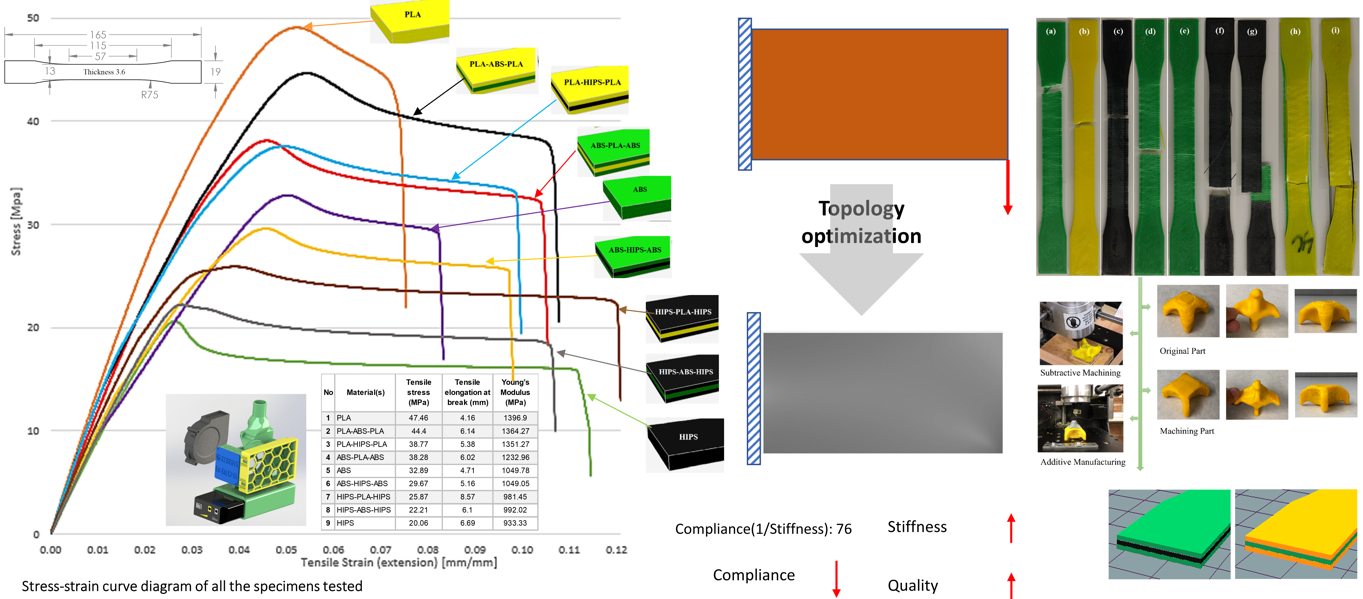
We are also testing different multi-material polymer structures and their topology optimization for various industrial applications.
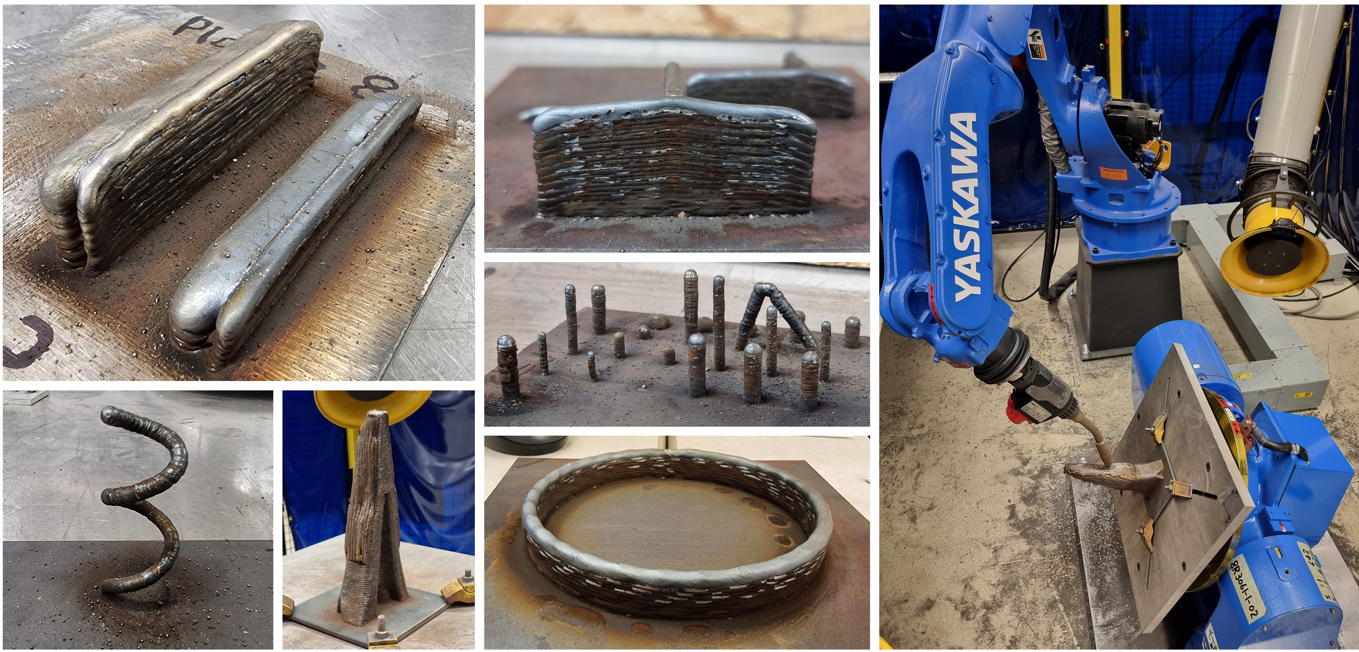

In collaboration with InnoTech Alberta, this project investigates path planning, repair, and Industry 4.0-related issues for Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM) process. WAAM is a process with the potential to supply industries with large form-factor prints at a deposition rate far greater than powder bed sintering that uses standard welding consumables to print solid metal parts with properties comparable to conventionally manufactured components. A 6-axis robot arm controls the CMT welding torch in conjunction with a 2-axis positioner to create 3D prints.
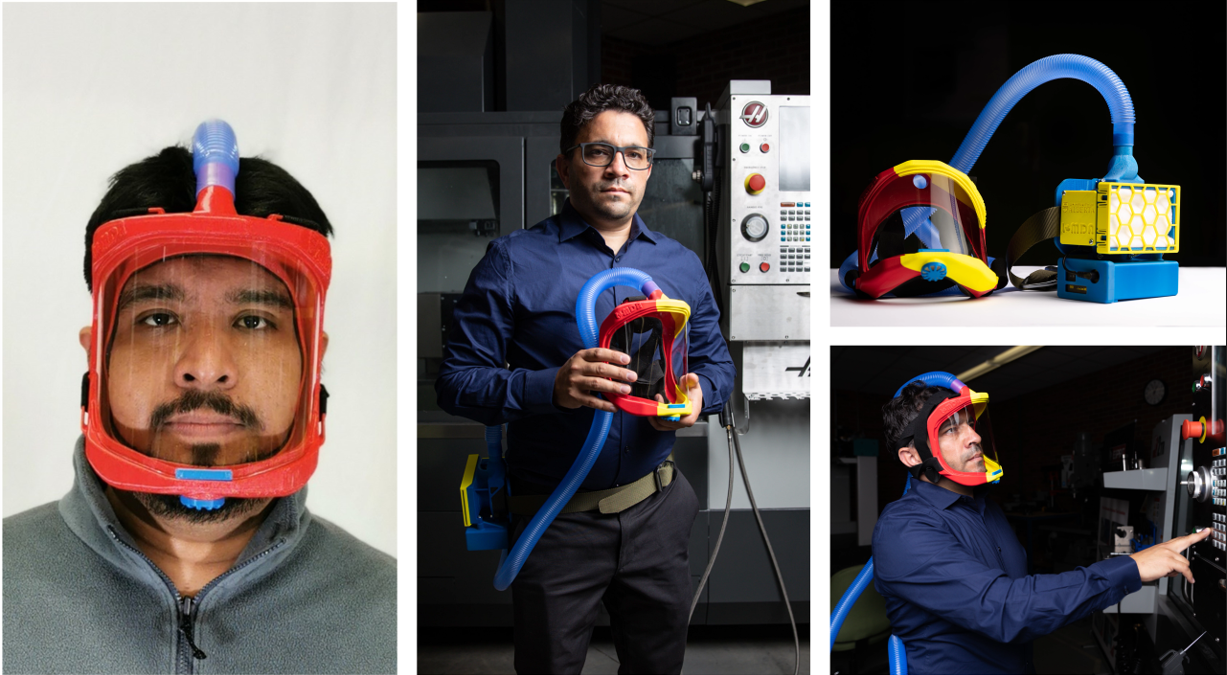

With the sudden advent of the COVID-19 pandemic, the lifestyle of everybody has changed. Doctors, nurses, and medical technicians are examples of front-liners who put their lives in danger for the welfare of others. Unfortunately, these professionals are the most needed on these adverse days and the ones most at risk. The PROPOS (https://thepropos.com/) is a personal protective respirator capable of shielding the user from COVID-19 microdroplets. This version is an open-source model manufactured by 3D printing technology. The device has two main components: an air gear with a washable A95 ACAMP filter and a battery lasting 12 hours. Second, an ergonomic face shield with defogging feature and an open-face and 180° vision screen for the user. This version is modular and can be reproduced and redesigned, adapting to any environmental, ergonomic, and comfortability constraints. The open-source design is available at the following link: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2468067221000523?via%3Dihub
This project investigates the role of coding in children’s education and the barriers to inclusion for Visually Impaired (VI) children in this environment. These children face numerous challenges in the learning process, including that most playful coding-related learning options rely on visualization. This project incorporates new design solutions based on the DODO model through computer vision, artificial intelligence, and tangible paper blocky modules for VI children to learn to code. The proof of concept prototype demonstrates that the proposed design can recognize the various paper modules used to represent different codes. The design advocates for VI children to have access to economic Science, Technology, Engineering, and Mathematics (STEM) learning. We are also investigating the use of plastic recycling in the DODO platform. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=r9_sK9ujFns&t=1s
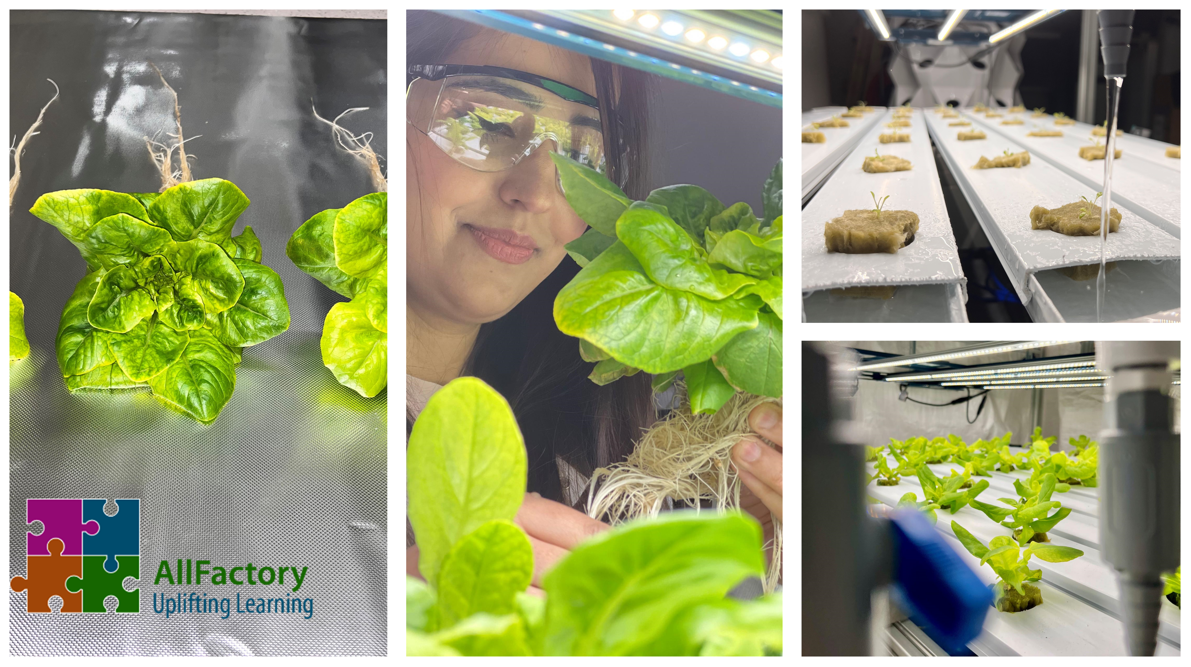

Aquaponics 4.0 Learning Factory (http://allfactory.ca/), also known as AllFactory, is the only learning factory in the world focusing on autonomous aquaponics from the engineering perspective. Dr. Rafiq Ahmad is the founder and director of AllFactory, initially established in 2019 at the University of Alberta. It is factory-in-a-lab transdisciplinary research, training, and learning factory investigating Aquaponics 4.0-related systems. AllFactory provides a unique Aquaponics vertical farming method and is a new sustainable and green farming technique that uses stacked layers of plants to improve plant yield per unit area while reducing required resources. Compared to conventional farming, vertical farming can result in a 70% reduction in water and fertilizer consumption per plant produced. Aquaponics combines aquaculture (farming of fish) and hydroponics (growing plants without soil), a technique to grow plants with aquaculture effluent. This technique claims to have a high water efficiency, is pesticide-free, and reduces the use of fertilizers.
Stay in touch with us to get latest news and discount coupons
Copyright © 2022 SMART LAB. All rights reserved.
