The average second level trigger rate of 100 Hz in ZEUS allows commercial micro-processors to be implemented at this stage. Transputers are the main processors used for front-end readout, data buffering, second level triggering and data acquisition by most components. In addition, transputers perform global second level trigger processing and combine the data from all the components into one global event (event-builder). Many components also use transputers for their monitoring.
The transputer network architectures vary from component to component within ZEUS. For example, the calorimeter second level trigger uses a regular tree-type network. The calorimeter readout and event-builder implement link switches to merge event data. On the other
[

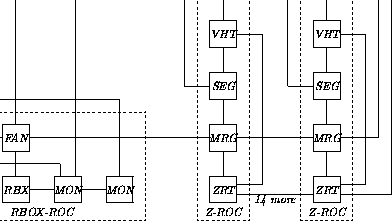
Fig. 2. The ZEUS central tracking detector readout and second level trigger system.
]
hand, the global second level trigger and central tracking detector transputer arrays are highly irregular networks. The central tracking detector uses the occam communication structure for merging processor data and fanning out the global second level trigger decision rather than link switches.
About 70% of the 250 000 electronic channels in the ZEUS experiment are read out by transputers and the entire transputer network currently consists of over 620 processors. The following is a brief description of some of the transputer arrays in the ZEUS experiment. Those transputer systems in ZEUS which are not mentioned have similar characteristics to those described here.