To build a bi-direction tri-state bus, you need to use two tri-state buffer for each bus line.
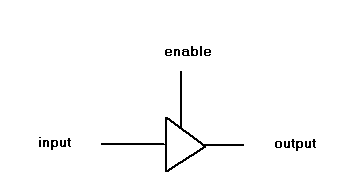
fig.1 A signal tri-state buffer

To build a bi-direction tri-state bus, you need
to use two tri-state buffer for each bus line.
fig.2 A bi-directional tri-state line
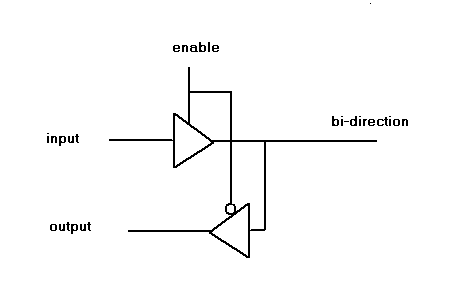
Notice the inverter on the bottom buffer, that allows the buffer have
an opposite enable signal from the upper one, ensuring the bus can only
be in either read or write state.
This setup only ensure one side of the bus, bus contention error can still occur if the opposite side is not synchronous with this side.
Here's a vhdl code that implements the tri-state bus above. It is obtained from the Altera web-site, and modified by our group to support optional bus width.