
Provides a terminal emulator for the X Window System.
Note: The xterm command is ported from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) X Window System, Version 11, Release 6 with no functional enhancements. The xterm command does not have support for localization or internationalization. For the localized and internationalized terminal emulator, the user can use the aixterm or dtterm commands.
xterm [ -ToolkitOption ... ] [ -Option ... ]
The xterm program is a terminal emulator for the X Window System. It provides DEC VT102 and Tektronix 4014 compatible terminals for programs that cannot use the window system directly. If the underlying operating system supports terminal resizing capabilities, the xterm program uses the facilities to notify programs running in the window whenever it is resized.
The VT102 and Tektronix 4014 terminals each have their own window so that you can edit text in one and look at graphics in the other at the same time. To maintain the correct aspect ratio (height/width), Tektronix graphics are restricted to the largest box with a 4014 aspect ratio that will fit in the window. This box is located in the upper left area of the window.
Although both windows may be displayed at the same time, one of them is considered the active window for receiving keyboard input and terminal output. This is the window that contains the text cursor. The active window can be chosen through escape sequences, the VT Options menu in the VT102 window, and the Tek Options menu in the 4014 window.
The VT102 emulation is fairly complete, but does not support smooth scrolling, VT52 mode, the blinking character attribute, or the double-wide and double-size character sets. The termcap file entries that work with the xterm command include xterm, vt102, vt100 and ``ansi,'' and the xterm command automatically searches the termcap file in this order for these entries and then sets the TERM and the TERMCAP environment variables.
Many of the special xterm features may be modified under program control through a set of escape sequences different from the standard VT102 escape sequences.
The Tektronix 4014 emulation is also fairly good. It supports 12-bit graphics addressing, scaled to the window size. Four different font sizes and five different lines types are supported. There is no write-thru or defocused mode support.
The Tektronix text and graphics commands are recorded internally by the xterm command and may be written to a file by sending the COPY escape sequence (or through the Tektronix menu, as described in the following sections). The name of the file will be COPYyy-MM-dd.hh:mm:ss, where yy, MM, dd, hh, mm, and ss are the year, month, day, hour, minute, and second when the copy is performed (the file is created in the directory that the xterm command is started in, or the home directory for a login xterm).
The xterm command automatically highlights the text cursor when the pointer enters the window (selected) and unhighlights it when the pointer leaves the window (unselected). If the window is the focus window, the text cursor is highlighted no matter where the pointer is located.
In VT102 mode, there are escape sequences to activate and deactivate an alternate screen buffer, which is the same size as the display area of the window. When activated, the current screen is saved and replaced with the alternate screen. Saving of lines scrolled off the top of the window is disabled until the normal screen is restored.
The termcap file entry for the xterm command allows the vi command editor to switch to the alternate screen for editing and to restore the screen on exit.
In either VT102 or Tektronix mode, there are escape sequences to change the name of the windows.
The xterm terminal emulator accepts all of the standard X Toolkit command-line options as well as the following (if the option begins with a + instead of a -, the option is restored to its default value):
The following command-line arguments are provided for compatibility with older versions. They may not be supported in the next release as the X Toolkit provides standard options that accomplish the same task.
The following standard X Toolkit command-line arguments are commonly used with the xterm command:
| -bg Color | Specifies the color to use for the background of the window. The default is white. |
| -bd Color | Specifies the color to use for the border of the window. The default is black. |
| -bw Number | Specifies the width in pixels of the border surrounding the window. |
| -fg Color | Specifies the color to use for displaying text. The default is black. |
| -fn Font | Specifies the font to be used for displaying normal text. The default is fixed. |
| -name Name | Specifies the application name under which resources are to be obtained, rather than the default executable file name. The Name parameter should not contain . or * characters. |
| -title String | Specifies the window title string, which may be displayed by window managers if the user so chooses. The default title is the command line specified after the -e option, if any; otherwise, the application name. |
| -rv | Indicates that reverse video should be simulated by swapping the foreground and background colors. |
| -geometry Geometry | Specifies the preferred size and position of the VT102 window; see the X command. |
| -display Display | Specifies the X server to contact; see the X command. |
| -xrm ResourceString | Specifies a resource string to be used. This is especially useful for setting resources that do not have separate command-line options. |
| -iconic | Indicates that the xterm command should ask the window manager to start it as an icon rather than as the normal window. |
The program understands all of the core X Toolkit resource names and classes as well as:
The following resources are specified as part of the vt100 widget (class VT100):
| allowSendEvents (class AllowSendEvents) | Specifies whether synthetic key and button events (generated using the X protocol SendEvent request) should be interpreted or discarded. The default is False, meaning they are discarded. Note that allowing such events creates a large security hole. | |
| alwaysHighlight (class AlwaysHighlight) | Specifies whether xterm should always display a highlighted text cursor. By default, a hollow text cursor is displayed whenever the pointer moves out of the window or the window loses the input focus. | |
| appcursorDefault (class AppcursorDefault) | ||
| If True, the cursor keys are initially in application mode. The default is False. | ||
| appkeypadDefault (class AppkeypadDefault) | ||
| If True, the keypad keys are initially in application mode. The default is False. | ||
| autoWrap (class AutoWrap) | Specifies whether auto wraparound should be enabled. The default is True. | |
| bellSuppressTime (class BellSuppressTime) | ||
| Specifies the number of milliseconds after a bell command is sent during which additional bells will be suppressed. The default is 200. If set to nonzero, additional bells will also be suppressed until the server reports that processing of the first bell has been completed; this feature is most useful with the visible bell. | ||
| boldFont (class BoldFont) | Specifies the name of the bold font to use instead of overstriking. | |
| c132 (class C132) | Specifies whether the VT102 DECCOLM escape sequence should be honored. The default is False. | |
| charClass (class CharClass) | Specifies comma-separated lists of character class bindings of the form [low-]high:value. These are used in determining which sets of characters should be treated the same when doing cut and paste. See "Character Classes". | |
| curses (class Curses) | Specifies whether the last column bug in the curses function should be worked around. The default is False. | |
| cutNewline (class cutNewline) | If false, triple clicking to select a line does not include the Newline at the end of the line. If true, the Newline is selected. The default is true. | |
| cutToBeginningofLines (class CutToBeginningOfLine) | ||
| If false, triple clicking to select a line selects only from the current word forward. If true, the entire line is selected. The default is true. | ||
| background (class Background) | Specifies the color to use for the background of the window. The default is white. | |
| foreground (class Foreground) | Specifies the color to use for displaying text in the window. Setting the class name instead of the instance name is an easy way to have everything that would normally appear in the text color change color. The default is black. | |
| cursorColor (class Foreground) | Specifies the color to use for the text cursor. The default is black. | |
| eightBitInput (class EightBitInput) | If True, meta characters input from the keyboard are presented as a single character with the eighth bit turned on. If False, meta characters are converted into a 2-character sequence with the character itself preceded by ESC. The default is True. | |
| eightBitOutput (class EightBitOutput) | Specifies whether 8-bit characters sent from the host should be accepted as is or stripped when printed. The default is True. | |
| font (class Font) | Specifies the name of the normal font. The default is fixed. | |
| font1 (class Font1) | Specifies the name of the first alternative font. | |
| font2 (class Font2) | Specifies the name of the second alternative font. | |
| font3 (class Font3) | Specifies the name of the third alternative font. | |
| font4 (class Font4) | Specifies the name of the fourth alternative font. | |
| font5 (class Font5) | Specifies the name of the fifth alternative font. | |
| font6 (class Font6) | Specifies the name of the sixth alternative font. | |
| geometry (class Geometry) | Specifies the preferred size and position of the VT102 window. | |
| hpLowerleftBugCompat (class hpLowerleftBugCompat) | ||
| Specifies whether to work around a bug in xdb, which ignores termcap and always sends ESC F to move to the lower left corner. true causes xterm in interpret ESC F as a request to move to the lower left corner of the screen. The default is false. | ||
| internalBorder (class BorderWidth) | Specifies the number of pixels between the characters and the window border. The default is 2. | |
| jumpScroll (class JumpScroll) | Specifies whether jump scrolling should be used. The default is True. | |
| loginShell (class LoginShell) | Specifies whether the shell to be run in the window should be started as a login shell. The default is False. | |
| marginBell (class MarginBell) | Specifies whether the bell should be run when the user types near the right margin. The default is False. | |
| multiClickTime (class MultiClickTime) | Specifies the maximum time in milliseconds between multiclick select events. The default is 250 milliseconds. | |
| multiScroll (class MultiScroll) | Specifies whether scrolling should be done asynchronously. The default is False. | |
| nMarginBell (class Column) | Specifies the number of characters from the right margin at which the margin bell should be rung, when enabled. | |
| pointerColor (class Foreground) | Specifies the foreground color of the pointer. The default is XtDefaultForeground. | |
| pointerColorBackground (class Background) | ||
| Specifies the background color of the pointer. The default is XtDefaultBackground. | ||
| pointerShape (class Cursor) | Specifies the name of the shape of the pointer. The default is xterm. | |
| resizeGravity (class ResizeGravity) | Affects the behavior when the window is resized to be taller or shorter. NorthWest specifies that the top line of text on the screen stays fixed. If the window is made shorter, lines are dropped from the bottom; if the window is made taller, blank lines are added at the bottom.
This is compatible with the behavior in MIT version X11R4. SouthWest (the default) specifies that the bottom line of text on the screen stays fixed. If the window is made taller, additional saved lines will be scrolled down onto the screen; if the window is made shorter, lines will be scrolled off the top of the screen, and the top saved lines will be dropped. | |
| reverseVideo (class ReverseVideo) | Specifies whether reverse video should be simulated. The default is False. | |
| reverseWrap (class ReverseWrap) | Specifies whether reverse wraparound should be enabled. The default is False. | |
| saveLines (class SaveLines) | Specifies the number of lines to save beyond the top of the screen when a scrollbar is turned on. The default is 64. | |
| scrollBar (class ScrollBar) | Specifies whether the scrollbar should be displayed. The default is False. | |
| scrollTtyOutput (class ScrollCond) | Specifies whether output to the terminal should automatically cause the scrollbar to go to the bottom of the scrolling region. The default is True. | |
| scrollKey (class ScrollCond) | Specifies whether pressing a key should automatically cause the scrollbar to go to the bottom of the scrolling region. The default is False. | |
| scrollLines (class ScrollLines) | Specifies the number of lines that the scroll-back and scroll-forw actions should use as a default. The default value is 1. | |
| signalInhibit (class SignalInhibit) | Specifies whether the entries in the Main Options menu for sending signals to xterm should be disallowed. The default is False. | |
| tekGeometry (class Geometry) | Specifies the preferred size and position of the Tektronix window. | |
| tekInhibit (class TekInhibit) | Specifies whether the escape sequence to enter Tektronix mode should be ignored. The default is False. | |
| tekSmall (class TekSmall) | Specifies whether the Tektronix mode window should start in its smallest size if no explicit geometry is given. This is useful when running the xterm command on displays with small screens. The default is False. | |
| tekStartup (class TekStartup) | Specifies whether xterm should start up in Tektronix mode. The default is False. | |
| titeInhibit (class TiteInhibit) | Specifies whether xterm should remove ti and te termcap file entries (used to switch between alternate screens during startup of many screen-oriented programs) from the TERMCAP string. If set, the xterm command also ignores the escape sequence to switch to the alternate screen. | |
| translations (class Translations) | Specifies the key and button bindings for menus, selections, programmed strings, and so forth. See "Actions". | |
| visualBell (class VisualBell) | Specifies whether a visible bell (flashing) should be used instead of an audible bell when the Ctrl-G key sequence signal is received. The default is False. | |
The following resources are specified as part of the tek4014 widget (class Tek4014):
The resources that may be specified for the various menus are described in the documentation for the Athena SimpleMenu widget. Following is a list of the names and classes of the entries in each of the menus.
The mainMenu has the following entries:
The vtMenu has the following entries:
The fontMenu has the following entries:
The tekMenu has the following entries:
The following resources are useful when specified for the Athena Scrollbar widget:
Once the VT102 window is created, the xterm command allows you to select text and copy it within the same or other windows.
The selection functions are invoked when the pointer buttons are used with no modifiers, and when they are used with the Shift key. The assignment of the functions to keys and buttons may be changed through the resource database.
Pointer button 1 (usually left) is used to save text into the cut buffer. Move the cursor to beginning of the text, and then hold the button down while moving the cursor to the end of the region and releasing the button. The selected text is highlighted and is saved in the global cut buffer and made the PRIMARY selection when the button is released.
Double-clicking selects by words, triple-clicking selects by lines, and quadruple-clicking goes back to characters. Multiple-click is determined by the amount of time from button up to button down, so you can change the selection unit in the middle of a selection. If the key or button bindings specify that an X selection is to be made, the xterm command will leave the selected text highlighted for as long as it is the selection owner.
Pointer button 2 (usually middle) "types" (pastes) the text from the PRIMARY selection, if any, otherwise from the cut buffer, inserting it as keyboard input.
Pointer button 3 (usually right) extends the current selection. If pressed while closer to the right edge of the selection than the left, it extends or contracts the right edge of the selection. If you contract the selection past the left edge of the selection, the xterm command assumes you really meant the left edge, restores the original selection, and then extends or contracts the left edge of the selection.
And the opposite also applies: if pressed while closer to the left edge of the selection than the right, it extends/contracts the left edge of the selection. If you contract the selection past the right edge of the selection, the xterm command assumes you really meant the right edge, restores the original selection, and then extends/contracts the right edge of the selection. Extension starts in the selection unit mode that the last selection or extension was performed in; you can multiple-click to cycle through them.
By cutting and pasting pieces of text without trailing new lines, you can take text from several places in different windows and form a command to the shell, for example, or take output from a program and insert it into your favorite editor. Since the cut buffer is globally shared among different applications, you should regard it as a "file" whose contents you know. The terminal emulator and other text programs should be treating it as if it were a text file; in other words, the text is delimited by new lines.
The scroll region displays the position and amount of text currently showing in the window (highlighted) relative to the amount of text actually saved. As more text is saved (up to the maximum), the size of the highlighted area decreases.
Clicking button 1 with the pointer in the scroll region moves the adjacent line to the top of the display window.
Clicking button 3 moves the top line of the display window down to the pointer position.
Clicking button 2 moves the display to a position in the saved text that corresponds to the pointer's position in the scrollbar.
Unlike the VT102 window, the Tektronix window does not allow the copying of text. It does allow Tektronix GIN mode, and in this mode the cursor will change from an arrow to a cross. Pressing any key will send that key and the current coordinates of the cross cursor. Pressing button one, two, or three will return the letters l, m, and r, respectively.
If the Shift key is pressed when a pointer button is pressed, the corresponding uppercase letter is sent. To distinguish a pointer button from a key, the high bit of the character is set (but this is bit is normally stripped unless the terminal mode is RAW; see the tty command for details).
The xterm command has four menus, named mainMenu, vtMenu, fontMenu, and tekMenu. Each menu pops up under the correct combinations of key and button presses. Most menus are divided into two section, separated by a horizontal line. The top portion contains various modes that can be altered. A check mark appears next to a mode that is currently active. Selecting one of these modes toggles its state. The bottom portion of the menu lists command entries; selecting one of these performs the indicated function.
The xterm menu pops up when the control key and pointer button one are pressed in a window. The mainMenu contains items that apply to both the VT102 and Tektronix windows. The Secure Keyboard mode is used when typing in passwords or other sensitive data in an unsecure environment.
Notable entries in the command section of the menu are Continue, Suspend, Interrupt, Hangup, Terminate, and Kill, which send the SIGCONT, SIGTSTP, SIGINT, SIGHUP, SIGTERM, and SIGKILL signals, respectively, to the process group of the process running under xterm (usually the shell). The Continue function is especially useful if the user has accidentally pressed Ctrl-Z, suspending the process.
The vtMenu sets various modes in the VT102 emulation, and is popped up when the control key and pointer button two are pressed in the VT102 window. In the command section of this menu, the soft reset entry will reset scroll regions. This can be convenient when some program has left the scroll regions set incorrectly (often a problem when using VMS or TOPS-20).
The full reset entry will clear the screen, reset tabs to every eight columns, and reset the terminal modes (such as wrap and smooth scroll) to their initial states just after the xterm command has finished processing the command-line options.
The fontMenu sets the font used in the VT102 window. In addition to the default font and a number of alternatives that are set with resources, the menu offers the font last specified by the Set Font escape sequence (See " Control Sequences" ) and the current selection as a font name (if the PRIMARY selection is owned).
The tekMenu sets various modes in the Tektronix emulation, and is popped up when the control key and pointer button two are pressed in the Tektronix window. The current font size is checked in the Modes section of the menu. The PAGE entry in the command section clears the Tektronix window.
X windows environments differ in their security consciousness. MIT servers, run under xdm, are capable of using a magic cookie authorization scheme that can provide a reasonable level of security for many people. If your server is only using a host-based mechanism to control access to the server (see the xhost command), and if you enable access for a host and other users are also permitted to run clients on that same host, there is every possibility that someone can run an application that will use the basic services of the X protocol to snoop on your activities, potentially capturing a transcript of everything you type at the keyboard.
This is of particular concern when you want to type in a password or other sensitive data. The best solution to this problem is to use a better authorization mechanism than host-based control, but a simple mechanism exists for protecting keyboard input in the xterm command.
The xterm menu contains a Secure Keyboard entry that, when enabled, ensures that all keyboard input is directed only to the xterm command (using the GrabKeyboard protocol request). When an application prompts you for a password (or other sensitive data), you can enable Secure Keyboard using the menu, type in the data, and then disable Secure Keyboard using the menu again.
Only one X client at a time can secure the keyboard, so when you attempt to enable Secure Keyboard it may fail. In this case, the bell will sound. If the Secure Keyboard succeeds, the foreground and background colors will be exchanged (as if you selected the Reverse Video entry in the Modes menu); they will be exchanged again when you exit secure mode. If the colors do not switch, you should be very suspicious that you are being spoofed.
If the application you are running displays a prompt before asking for the password, it is safest to enter secure mode before the prompt gets displayed, and to make sure that the prompt gets displayed correctly (in the new colors), to minimize the probability of spoofing. You can also bring up the menu again and make sure that a check mark appears next to the entry.
Secure Keyboard mode will be disabled automatically if your xterm window becomes iconified (or otherwise unmapped), or if you start up a reparenting window manager (that places a title bar or other decoration around the window) while in Secure Keyboard mode. (This is a feature of the X protocol not easily overcome.) When this happens, the foreground and background colors will be switched back and the bell will sound in warning.
Clicking the middle mouse button twice in rapid succession will cause all characters of the same class (such as letters, white space, punctuation) to be selected. Since different people have different preferences for what should be selected (for example, should file names be selected as a whole or only the separate subnames), the default mapping can be overridden through the use of the charClass (class CharClass) resource.
This resource is a series of comma-separated range:value pairs. The range is either a single number or low-high in the range of 0 to 127, corresponding to the ASCII code for the character or characters to be set. The value is arbitrary, although the default table uses the character number of the first character occurring in the set.
static int charClass[128] = {
/* NUL SOH STX ETX EOT ENQ ACK BEL */
32, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
/* BS HT NL VT NP CR SO SI */
1, 32, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
/* DLE DC1 DC2 DC3 DC4 NAK SYN ETB */
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
/* CAN EM SUB ESC FS GS RS US */
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
/* SP ! " # $ % & ' */
32, 33, 34, 35, 36, 37, 38, 39,
/* ( ) * + , - . / */
40, 41, 42, 43, 44, 45, 46, 47,
/* 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 */
48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48,
/* 8 9 : ; < = > ? */
48, 48, 58, 59, 60, 61, 62, 63,
/* @ A B C D E F G */
64, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48,
/* H I J K L M N O */
48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48,
/* P Q R S T U V W */
48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48,
/* X Y Z [ \ ] ^ _ */
48, 48, 48, 91, 92, 93, 94, 48,
/* ` a b c d e f g */
96, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48,
/* h i j k l m n o */
48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48,
/* p q r s t u v w */
48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48, 48,
/* x y z { | } ~ DEL */
48, 48, 48, 123, 124, 125, 126, 1};
For example, the string 33:48,37:48,45-47:48,64:48 indicates that the exclamation mark, percent sign, dash, period, slash, and ampersand characters should be treated the same way as characters and numbers. This is useful for cutting and pasting electronic mailing addresses and file names.
It is possible to rebind keys (or sequences of keys) to arbitrary strings for input by changing the translations for the vt100 or tek4014 widgets. Changing the translations for events other than key and button events is not expected, and will cause unpredictable behavior. The following actions are provided for using within the vt100 or tek4014 translations resources:
| bell([Percent]) | This action rings the keyboard bell at the specified percentage above or below the base volume. |
| ignore() | This action ignores the event but checks for special pointer position escape sequences. |
| insert() | This action inserts the character or string associated with the key that was pressed. |
| insert-seven-bit() | This action is a synonym for insert(). |
| insert-eight-bit() | This action inserts an 8-bit (meta) version of the character or string associated with the key that was pressed. The exact action depends on the value of the eightBitInput resource. |
| insert-selection(SourceName [, ...]) | |
| This action inserts the string found in the selection or cutbuffer indicated by the SourceName parameter. Sources are checked in the order given (case is significant) until one is found. Commonly used selections include PRIMARY, SECONDARY, and CLIPBOARD. Cut buffers are typically named CUT_BUFFER0 through CUT_BUFFER7. | |
| keymap(Name) | This action dynamically defines a new translation table whose resource name is Name with the suffix Keymap (case is significant). The name None restores the original translation table. |
| popup-menu(MenuName) | This action displays the specified popup menu. Valid names (case is significant) include mainMenu, vtMenu, fontMenu, and tekMenu. |
| secure() | This action toggles the Secure Keyboard mode described in the section named " Security", and is invoked from the securekbd entry in mainMenu. |
| select-start() | This action begins text selection at the current pointer location. See the section entitled " Pointer Usage " for information on making selections. |
| select-extend() | This action tracks the pointer and extends the selection. It should only be bound to Motion events. |
| select-end(DestName [, ...]) | |
| This action puts the currently selected text into all of the selections or cutbuffers specified by DestName. | |
| select-cursor-start() | This action is similar to select-start except that it begins the selection at the current text cursor position. |
| select-cursor-end(DestName [, ...]) | |
| This action is similar to select-end except that it should be used with select-cursor-start. | |
| set-vt-font(d/1/2/3/4/5/6/e/s [,NormalFont [, BoldFont]]) | |
| This action sets the font or fonts currently being used in the VT102 window. The first argument is a single character that specifies the font to be used:
d or D indicates the default font (the font initially used when the xterm command was started), 1 through 6 indicate the fonts specified by the font1 through font6 resources, e or E indicates the normal and bold fonts that have been set through escape codes (or specified as the second and third action arguments, respectively), and s or S indicates the font selection (as made by programs such as the xfontsel program) specified by the second action argument. | |
| start-extend() | This action is similar to select-start except that the selection is extended to the current pointer location. |
| start-cursor-extend() | This action is similar to select-extend except that the selection is extended to the current text cursor position. |
| string(String) | This action inserts the specified text string as if it had been typed. Quotation is necessary if the string contains white space or nonalphanumeric characters. If the string argument begins with the characters ``0x,'' it is interpreted as a hex character constant. |
| scroll-back(Count [,Units]) | |
| This action scrolls the text window backward so that text that had previously scrolled off the top of the screen is now visible. The Count argument indicates the number of Units (which may be page, halfpage, pixel, or line) by which to scroll. | |
| scroll-forw(Count [,Units]) | |
| This action scrolls is similar to scroll-back except that it scrolls the other direction. | |
| allow-send-events(On/Off/Toggle) | This action set or toggles the allowSendEvents resource and is also invoked by the allowsends entry in mainMenu. |
| redraw() | This action redraws the window and is also invoked by the redraw entry in mainMenu. |
| send-signal(SigName) | This action sends the signal named by SigName to the xterm subprocess (the shell or program specified with the -e command-line option) and is also invoked by the suspend, continue, interrupt, hangup, terminate, and kill entries in mainMenu. Allowable signal names are (case is not significant): |
| quit() | This action sends a SIGHUP to the subprogram and exits. It is also invoked by the quit entry in mainMenu. |
| set-scrollbar(On/Off/Toggle) | This action toggles the scrollbar resource and is also invoked by the scrollbar entry in vtMenu. |
| set-jumpscroll(On/Off/Toggle) | This action toggles the jumpscroll resource and is also invoked by the jumpscroll entry in vtMenu. |
| set-reverse-video(On/Off/Toggle) | This action toggles the reverseVideo resource and is also invoked by the reversevideo entry in vtMenu. |
| set-autowrap(On/Off/Toggle) | This action toggles automatic wrapping of long lines and is also invoked by the autowrap entry in vtMenu. |
| set-reversewrap(On/Off/Toggle) | This action toggles the reverseWrap resource and is also invoked by the reversewrap entry in vtMenu. |
| set-autolinefeed(On/Off/Toggle) | This action toggles automatic insertion of linefeeds and is also invoked by the autolinefeed entry in vtMenu. |
| set-appcursor(On/Off/Toggle) | This action toggles the handling Application Cursor Key mode and is also invoked by the appcursor entry in vtMenu. |
| set-appkeypad(On/Off/Toggle) | This action toggles the handling of Application Keypad mode and is also invoked by the appkeypad entry in vtMenu. |
| set-scroll-on-key(On/Off/Toggle) | This action toggles the scrollKey resource and is also invoked from the scrollkey entry in vtMenu. |
| set-scroll-on-tty-output(On/Off/Toggle) | |
| This action toggles the scrollTtyOutput resource and is also invoked from the scrollttyoutput entry in vtMenu. | |
| set-allow132(On/Off/Toggle) | This action toggles the c132 resource and is also invoked from the allow132 entry in vtMenu. |
| set-cursesemul(On/Off/Toggle) | This action toggles the curses resource and is also invoked from the cursesemul entry in vtMenu. |
| set-visual-bell(On/Off/Toggle) | This action toggles the visualBell resource and is also invoked by the visualbell entry in vtMenu. |
| set-marginbell(On/Off/Toggle) | This action toggles the marginBell resource and is also invoked from the marginbell entry in vtMenu. |
| set-altscreen(On/Off/Toggle) | This action toggles between the alternate and current screens. |
| soft-reset() | This action resets the scrolling region and is also invoked from the softreset entry in vtMenu. |
| hard-reset() | This action resets the scrolling region, tabs, window size, and cursor keys and clears the screen. It is also invoked from the hardreset entry in vtMenu. |
| clear-saved-lines() | This action does hard-reset (see previous entry) and also clears the history of lines saved off the top of the screen. It is also invoked from the clearsavedlines entry in vtMenu. |
| set-terminal-type(Type) | This action directs output to either the vt or tek windows, according to the Type string. It is also invoked by the tekmode entry in vtMenu and the vtmode entry in tekMenu. |
| set-visibility(vt/tek, On/Off/Toggle) | |
| This action controls whether or not the vt or tek windows are visible. It is also invoked from the tekshow and vthide entries in vtMenu and the vtshow and tekhide entries in tekMenu. | |
| set-tek-text(large/2/3/small) | This action sets font used in the Tektronix window to the value of the resources tektextlarge, tektext2, tektext3, and tektextsmall according to the argument. It is also by the entries of the same names as the resources in tekMenu. |
| tek-page() | This action clears the Tektronix window and is also invoked by the tekpage entry in tekMenu. |
| tek-reset() | This action resets the Tektronix window and is also invoked by the tekreset entry in tekMenu. |
| tek-copy() | This action copies the escape codes used to generate the current window contents to a file in the current directory beginning with the name COPY. It is also invoked from the tekcopy entry in tekMenu. |
| visual-bell() | This action flashes the window quickly. |
The Tektronix window also has the following action:
| gin-press(l/L/m/M/r/R) | This action sends the indicated graphics input code. |
The default bindings in the VT102 window are:
Shift <KeyPress> Prior: scroll-back(1,halfpage) \n\
Shift <KeyPress> Next: scroll-forw(1,halfpage) \n\
Shift <KeyPress> Select: select-cursor-start \
select-cursor-end(PRIMARY,
CUT_BUFFER0) \n\
Shift <KeyPress> Insert: insert-selection(PRIMARY,
CUT_BUFFER0) \n\
~Meta<KeyPress>: insert-seven-bit \n\
Meta<KeyPress>: insert-eight-bit \n\
!Ctrl <Btn1Down>: popup-menu(mainMenu) \n\
!Lock Ctrl <Btn1Down>: popup-menu(mainMenu) \n\
~Meta <Btn1Down>: select-start \n\
~Meta <Btn1Motion>: select-extend \n\
!Ctrl <Btn2Down>: popup-menu(vtMenu) \n\
!Lock Ctrl <Btn2Down>: popup-menu(vtMenu) \n\
~Ctrl ~Meta <Btn2Down>: ignore \n\
~Ctrl ~Meta <Btn2Up>: insert-selection(PRIMARY,
CUT_BUFFER0) \n\
!Ctrl <Btn3Down>: popup-menu(fontMenu) \n\
!Lock Ctrl <Btn3Down>: popup-menu(fontMenu) \n\
~Ctrl ~Meta <Btn3Down>: start-extend \n\
~Meta <Btn3Motion>: select-extend \n\
<BtnUp>: select-end(PRIMARY, CUT_BUFFER0) \n\
<BtnDown>: bell(0)
The default bindings in the Tektronix window are:
~Meta<KeyPress>: insert-seven-bit \n\ Meta<KeyPress>: insert-eight-bit \n\ !Ctrl <Btn1Down>: popup-menu(mainMenu) \n\ !Lock Ctrl <Btn1Down>: popup-menu(mainMenu) \n\ !Ctrl <Btn2Down>: popup-menu(tekMenu) \n\ !Lock Ctrl <Btn2Down>: popup-menu(tekMenu) \n\ Shift ~Meta<Btn1Down>: gin-press(L) \n\ ~Meta<Btn1Down>: gin-press(l) \n\ Shift ~Meta<Btn2Down>: gin-press(M) \n\ ~Meta<Btn2Down>: gin-press(m) \n\ Shift ~Meta<Btn3Down>: gin-press(R) \n\ ~Meta<Btn3Down>: gin-press(r)
The following is an example of how the keymap action is used to add special keys for entering commonly typed works:
*VT100.Translations: #override <Key>F13: keymap(dbx)
*VT100.dbxKeymap.translations:
\
<Key>F14: keymap(None) \n\
<Key>F17: string("next") string(0x0d) \n\
<Key>F18: string("step") string(0x0d) \n\
<Key>F19: string("continue") string(0x0d) \n\
<Key>F20: string("print ")
insert-selection(PRIMARY,CUT_BUFFER0)
The xterm command sets the environment variables TERM and TERMCAP properly for the size window you have created. It also uses and sets the DISPLAY environment variable to specify which bitmap display terminal to use. The WINDOWID environment variable is set to the X window ID number of the xterm window.
Large pastes do not work on some systems. This is not a bug in the xterm command; it is a bug in the pseudo terminal driver of those systems. The xterm command feeds large pastes to the pty only as fast as the pty will accept data, but some pty drivers do not return enough information to know if the write operation has succeeded.
Many of the options are not resettable after the xterm command starts.
Only fixed-width, character-cell fonts are supported.
This section lists control sequences available for the xterm command.
The following figure shows how to interpret key sequences in this section.

Most of these control sequences are standard VT102 control sequences, but there are some sequences here from later DEC VT terminals, too. Major VT102 features not supported are smooth scrolling, double-size characters, blinking characters, and VT52 mode.
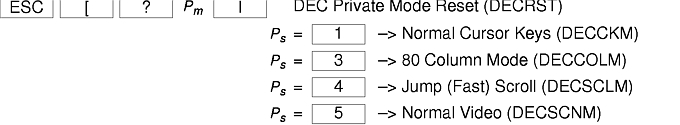
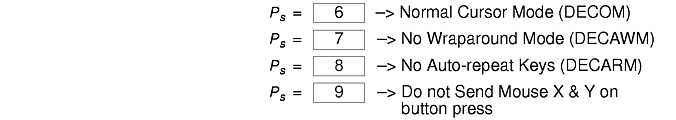
There are additional control sequences to provide xterm-dependent functions, like the scrollbar or window size. Where the function is specified by DEC or ISO 6429, the code assigned to it is given in parentheses. The escape codes to designate character sets are specified by ISO 2022; see that document for a discussion of character sets.


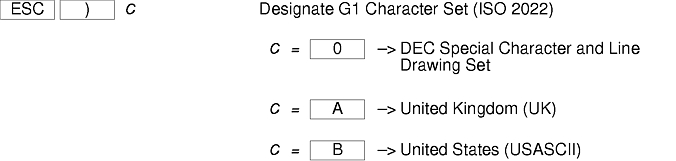
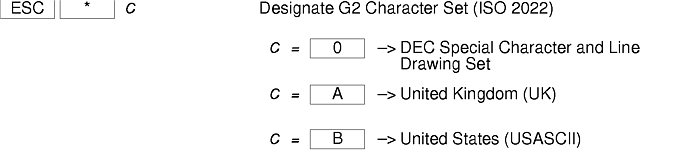
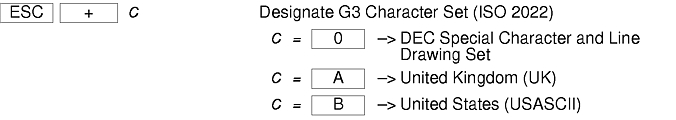



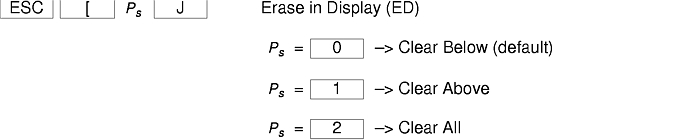
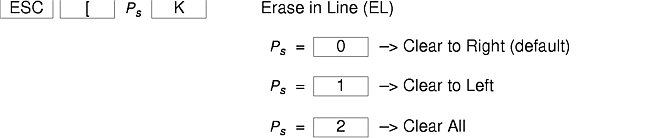

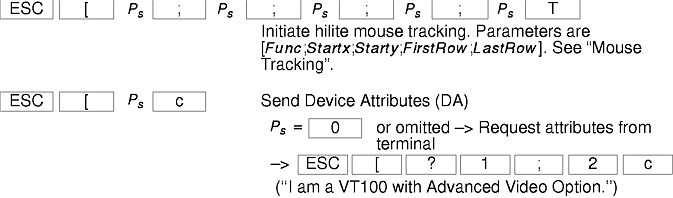
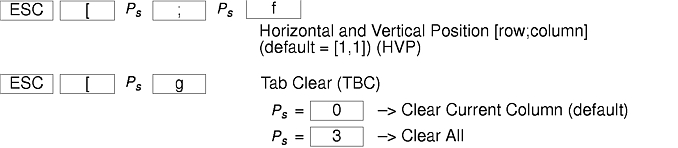
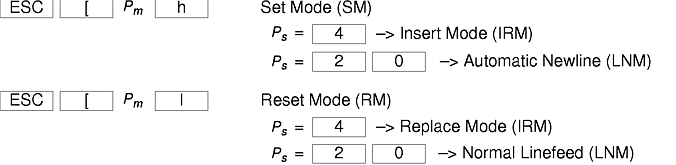
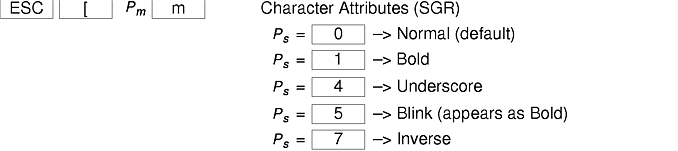
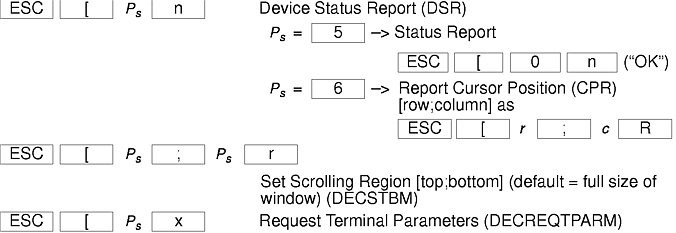
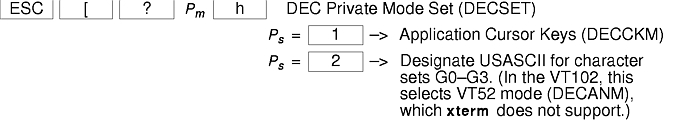
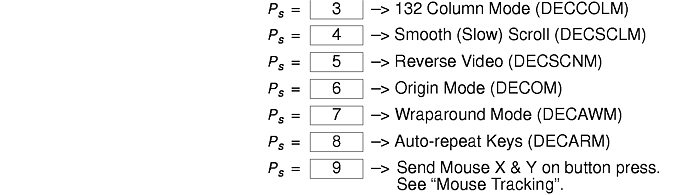



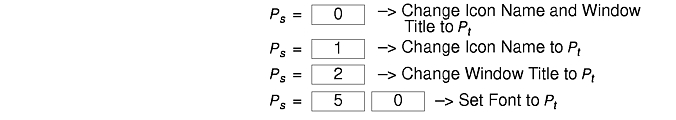



The xterm terminal description in the DEC.TI file on AIX Version 4 provides underline mode by using the SGR attribute. The SMUL and RMUL attributes are not currently defined in the XTERM terminal description on AIX Version 4. Use the more generic capability named SGR.
tput sgr x y
Where x is either a 1 or a 0 to turn standout mode on or off respectively, and y is either a 1 or a 0 to turn underline mode on or off respectively. See the article "terminfo file format" for more details on the SGR capability.
tput sgr 0 1 turn off standout; turn on underline tput sgr 0 0 turn off standout; turn off underline tput sgr 1 1 turn on standout; turn on underline tput sgr 1 0 turn on standout; turn off underline
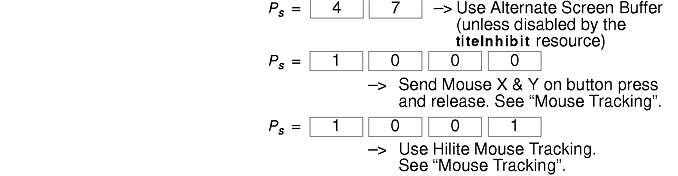
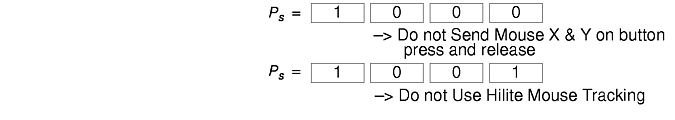
The VT widget can be set to send the mouse position and other information on button presses. These modes are typically used by editors and other full-screen applications that want to make use of the mouse.
There are three mutually exclusive modes, each enabled (or disabled) by a different parameter in the DECSET (or DECRST) escape sequence. Parameters for all mouse tracking escape sequences generated by the xterm command encode numeric parameters in a single character as value+040. The screen coordinate system is 1-based.
X10 compatibility mode sends an escape sequence on button press encoding the location and the mouse button pressed. It is enabled by specifying parameter 9 to DECSET. On button press, the xterm command sends the following 6 characters. Cb is button-1. Cx and Cy are the x and y coordinates of the mouse when the button was pressed.

Normal tracking mode sends an escape sequence on both button press and release. Modifier information is also sent. It is enabled by specifying parameter 1000 to DECSET. On button press or release, the xterm command sends the following key sequence:

The low two bits of Cb encode button information: 0=MB1 pressed, 1=MB2 pressed, 2=MB3 pressed, 3=release. The upper bits encode what modifiers were down when the button was pressed and are added together. 4=Shift, 8=Meta, 16=Control. Cx and Cy are the x and y coordinates of the mouse event. The upper left corner is (1,1).
Mouse hilite tracking notifies a program of a button press, receives a range of lines from the program, highlights the region covered by the mouse within that range until button release, and then sends the program the release coordinates. It is enabled by specifying parameter 1001 to DECSET.
Attention: Use of this mode requires a cooperating program or it will hang the xterm command. On button press, the same information as for normal tracking is generated; the xterm command then waits for the program to send mouse tracking information. All X events are ignored until the following proper escape sequence is received from the pty:

The parameters are Func, Startx, Starty, FirstRow, and LastRow. The Func parameter is nonzero to initiate hilite tracking and 0 (zero) to abort. The Startx and Starty parameters give the starting x and y location for the highlighted region. The ending location tracks the mouse, but is never above row FirstRow and is always above row LastRow. (The top of the screen is row 1.) When the button is released, the xterm command reports the ending position one of two ways: if the start and end coordinates are valid text locations, the xterm command reports the ending position as follows:

If either coordinate is past the end of the line, the xterm command reports the ending position as follows:

The parameters are Startx, Starty, Endx, Endy, Mousex, and Mousey. The Startx, Starty, Endx, and Endy parameters give the starting and ending character positions of the region. The Mousex and Mousey parameters give the location of the mouse at button up, which may not be over a character.
Most of these sequences are standard Tektronix 4014 control sequences. The major features missing are the write-thru and defocused modes. This document does not describe the commands used in the various Tektronix plotting modes but does describe the commands to switch modes.
The aixterm command, resize command, tset command, vi or vedit command.