
1. What is prompting?
2. What are the different kinds of response prompts and stimulus prompts?
3. Explain transfer of stimulus control.
4. Describe the ways of transferring stimulus control.
5. What is the procedure for using prompting and transfer of stimulus control?
How can prompting be used to teach self-feeding more quickly than _______?
(Sarafino, 2012)
- Jan, a 3-year-old with mild developmental disability and a neurological disorder that made it difficult to perform motor actions
- she could not feed herself with a _____
- behavioural treatment program:
• started at lunchtime, when Jan had not _____ for several hours
• behaviour analyst began by saying, “Look at what I do” and pointed at a plate of food
• next, he took a spoon, scooped some food, and lifted it to his mouth
• then, he put the spoon in Jan’s hand, and grasped her hand to guide it
• he scooped food, saying “Scoop some food” and “Put it in your mouth” while _______ her perform those actions
• when this was successfully accomplished, he praised Jan, saying “Good job eating!”
- these shortcut methods modify ___________ instead of using shaping
- after some repetitions, the behaviour analyst moved his hand from Jan’s hand to her wrist, then her elbow, then did not contact her at all
- results:
• eventually, spoken instructions were reduced and eliminated when Jan was able to perform the target behaviour on her own
- definition: giving _______ before (or during) performance of a behaviour to increase the likelihood that a person will engage in the target behaviour at the correct time
- prompts supplement the SD or modify it to make it more salient (or make the SΔ less salient)
Types of Prompts:
- ________ prompt: behaviour of another person that evokes the target behaviour from the target person when the SD is also present; prompts may vary in intrusiveness
• ______ prompt: hints, instructions, commands, or other spoken words used to guide or direct behaviour
e.g., telling a child, “Scoop some food”
• ________ prompt: physical movements that indicate how, where, or what behaviour to perform
e.g., parent pointing to food and child’s mouth
e.g., when my kids ask for something, I tap my ear until they say “Please?”
• ________ prompt: demonstration of the entire target behaviour by another person
e.g., parent uses spoon to scoop and eat some food
• physical ________ prompt: another person physically assists in the execution of the target behaviour
e.g., grasping a child’s hand to help her put spoonful of food to her mouth
• _____-____ prompting: use prompts progressively, starting with verbal, then modeling, and finally physical guidance prompts
- ________ prompt: SD is changed (within-stimulus), or stimulus is added (extra-stimulus) or removed, to encourage the target behaviour
• ______-stimulus prompt: involves changing the SD in some way (change location of the SD, or change some dimension of the SD, such as size, shape, color, or intensity)
• _____-stimulus prompt: involves adding a stimulus to the SD
- stimulus prompts can also be divided into types:
• _______ prompts: drawings or photos
e.g., symbols on computer keys 
• ________ prompts: sounds (other than words)
e.g., auditory alarm that detects first drops of urine used to help children with severe developmentally disability learn toileting behaviours
• _____________ prompts: alterations or additions to the physical surroundings in which the SD is presented
e.g., changing the seating arrangement in a classroom
- definition: _______ are faded, reduced, or eliminated so that target behaviour occurs to the SD alone; behaviour continues to be reinforced
Fading: gradual ___________ of prompting so that eventually it is no longer needed; stimulus control is transferred from prompts to SD
e.g., after sufficient repetitions, Jan was able to use a spoon to eat without physical help, then eventually without verbal prompts
- ________ prompt fading (or prompt fading): response prompt is gradually lessened
• fading ______ prompt: same prompt is used, but is decreased in magnitude
e.g., teacher shows a flash card with the word blueberry, and her prompts are reduced from saying “blueberry” to “blue-” to “b-”
• fading ______ prompts: prompt is changed, according to a prompting hierarchy
▸ ____-__-_____ prompting and fading (a.k.a. decreasing assistance): prompts change from more intrusive to less intrusive (physical guidance > modeling > gestural > verbal)
- start with most intrusive prompt
- when target behaviour occurs reliably, move to next less intrusive prompt in the next session
- used when initially teaching a skill and person likely needs physical guidance prompt
▸ _____-__-____ prompting and fading (a.k.a. increasing assistance, or system of least prompts): prompts change from less to more intrusive (like in three-step prompting) until behaviour is performed
- start with least intrusive prompt
- provide more intrusive prompts, if required, in the same session
- used when person has learned the skill and may not need physical guidance prompt
- _________ guidance: used in fading physical guidance prompts; teacher provides as much physical guidance as required, and then gradually reduces it:
• pressure/contact may be reduced
• _________: teacher’s hand follows learner’s movement without contact
• _______ fading: focus of guidance (teacher’s hand contact) changes from fingers, to hand, to wrist, to elbow, etc.
e.g., children with disability first given hand over hand prompting, next time given manual guidance at forearm, then manual guidance at upper arm, then light touch/shadow, until they could independently build a Lego structure (Libby et al., 2008)
- ________ prompt fading (or stimulus fading): stimulus prompt is decreased in magnitude or frequency
e.g., 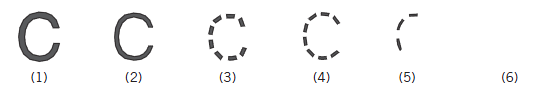
Prompt _____: present SD, wait a certain number of seconds, and if target behaviour does not occur, provide the prompt
- time delay may be constant, or progressive (increasing duration of intervals)
- typically used only with response prompts
e.g., present flash card with a word on it, wait for person to say the word
If they do not say it in 4 seconds, a verbal prompt is given.
1. choose most ___________ prompting strategy
- use prompting only when the person has not learned to perform the target behaviour with the SD
- or has not learned to perform the behaviour in the correct situation
- prompting is not appropriate when behaviour is not produced due to noncompliance
2. get learner’s _________
- make SD more salient, or SΔ less salient
3. always present the SD
4. ______ correct response if SD does not evoke it
- response prompts are most useful for helping a person learn a specific action or sequence of actions (e.g., tying shoelaces)
- stimulus prompts are most useful for helping a person learn to discriminate stimuli (e.g., letters of the alphabet)
- if person has developmental disabilities/limited abilities, more _________ prompts will be needed
- if person can understand verbal prompts, describe reasons for the behaviour in terms of the natural consequences
e.g., “If you swat that bee, it will sting you”
5. _________ correct behaviour
6. ________ stimulus control
- size of fading steps should be appropriate
- if step is too big, the behaviour is incorrect and will not be reinforced
- too small, and the person will become dependent on the prompt
- solution: promote _________ learning: at each step, just enough of a prompt is given so that the person makes no errors in performing the task
7. continue to _________ unprompted responses