1. What is extinction, and how does it come about?
2. What are three “side effects” of extinction?
3. List the factors that influence extinction.
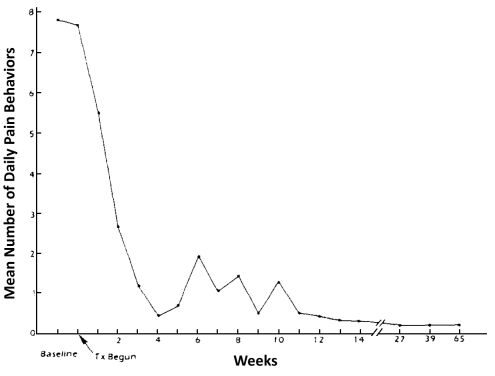
How can migraine headaches be modified by extinction?
(Aubuchon et al., 1985)
- Louise, a 26-year-old woman, had migraine headaches since age 13
- received parental attention for her headaches; was allowed to stay home from school
- no _______ cause could be determined
- treated unsuccessfully with acupuncture, chiropractic, psychotherapy, and electroconvulsive shock
- temporary relief provided by narcotic _________ Demerol® (meperidine) three times a week
- behavioural treatment program (with Louise’s consent):
• no further medication provided
• baseline recording of her pain behaviours (e.g., complaints, going to bed)
• parents, husband, doctor, and nurses _______ pain behaviours
• they gave praise for well behaviours (e.g., work, exercise, domestic chores)
- results: pain behaviours substantially decreased
- definition: if a behaviour that was previously reinforced stops being reinforced, the behaviour will ______ or decrease
- works with behaviour previously maintained with positive reinforcement:
e.g., student doing addition reversed the digits (7+5=21); teacher stopped explaining the error and giving extra attention; reversals decreased
- or behaviour maintained with negative reinforcement:
e.g., child did not want to be in school and had tantrums; parents stopped taking child out of school; tantrums decreased
- not the same as __________ a behaviour
• extinction _____: behaviour may briefly increase in frequency, duration, or intensity after the reinforcement is eliminated
e.g., child swears: parents ignore it; swearing increases before declining
• extinction-induced __________: novel behaviours, often emotional or aggressive, may be exhibited
e.g., failing to receive attention for swearing, child throws a toy on the ground and screams
• ___________ recovery: after a period of extinction, a behaviour may reappear, despite the lack of reinforcement
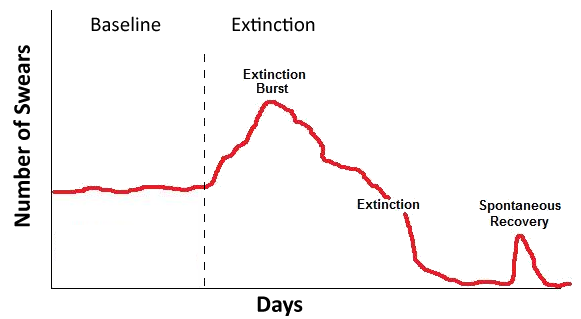
(Note: textbook considers novel behaviours to be part of extinction burst, not extinction-induced aggression.)
• previous schedule of reinforcement:
- continuous schedule leads to faster decrease in behaviour (lower __________ to extinction or RTE)
- intermittent schedule leads to slower decrease in behaviour (greater RTE)
e.g., in the past, sometimes ignoring to child’s swearing, but sometimes attending to it → greater RTE
• _________ of previous reinforcement: larger reinforcer produces greater RTE
• inadvertent reinforcement that occurs during the extinction phase → behaviour increases
• extinction of unwanted behaviour should be combined with reinforcement of a ____________ __________ alternative behaviour (i.e., gives them the same reinforcement)
e.g., if a child swears to get attention, then give them attention for using appropriate language