 Alberta's WaterIntroductionPublications Climate Change Industrial Impacts Agricultural Impacts Urban Impacts Biodiversity Loss Definitions Links Site Map |
 |
|
 |
 |
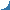
| A sign for the pipeline that failed | The number of pipeline failures in Alberta (EUB) |
The Energy and Utilities Board (EUB) of Alberta reports approximately 700 pipeline failures every year which vary from small leaks to large ruptures, resulting in loss of the substance being transported. These failures typically occur in flowlines and gathering lines that link wells to oil batteries where water and impurities are removed. Pipeline failures are primarily due to internal corrosion from water and multiphase oil. Multiphase oil pipelines can carry unprocessed petroleum, minerals, salt water and natural gas with hydrogen sulfide. Water pipelines carry fresh or saline water removed from the oil (produced water), or surface or groundwater that is injected in wells to displace oil to the surface. In 2002, the total reported spill volumes of hydrocarbon and produced water by companies operating in the province were 5,189 m3 and 19,165 m3, respectively. To prevent product loss from the predominantly steel pipelines, chemicals that reduce corrosion and accumulated debris are widely used. While it is known that hydrocarbons and salts can harm the environment, to our knowledge, there are no experimental studies or field reports on the effects of pipeline maintenance chemicals - clear liquids that may appear harmless in a freshwater spill.


 Impacts of a Petroleum Pipeline Failure in the Alberta Foothills
Impacts of a Petroleum Pipeline Failure in the Alberta Foothills