Welcome to the University of Alberta's Engineering Program Plan Visualizer.
On this page, you will find all of the information found on the University Calendar, presented in an easier to understand format.
There are some features you should be aware of:
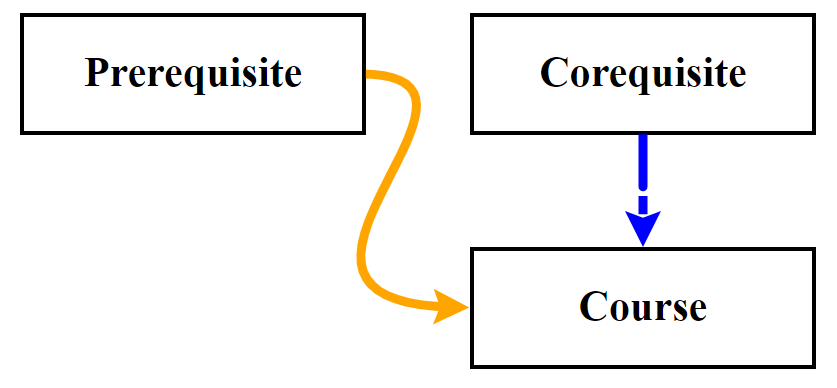
- Hover over a course to see its Calendar description pop-up.
- Left click on a course to draw arrows between that course and its prerequisites and corequisites, as well as the courses it is a prerequisite and corequisite for.
- Right click on a course to have its Calendar description stay in place.
- Switch the ordering of course groups by toggling the buttons to the right of the selected plan. The selected course group will be displayed first (before the other course group).
- Switch between plans by toggling the buttons below "Plan".
- Highlight all courses in a category by left-clicking on one of the colored boxes to the right of the course group selector.
- To clear all selections, refresh the page.
Plan
Fall Term 1
CHEM 103
★ 4.3
(fi 6)(either term,
3-1s-3/2)
Atoms and molecules, states of matter, chemistry of the elements. Prerequisite: Chemistry 30, or equivalent. Note: Restricted to Engineering students only. Other students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 53.5 Units
ENGG 100
★ 1.1
(fi 2)(either term,
.75-.75s-0)
An introduction to the Faculty of Engineering, the engineering profession, the skills required for academic success, and the fundamentals of leadership: study and life skills; time management and goal setting; interpersonal skills; career planning; engineering and society including elements of ethics, equity, concepts of sustainable development, environmental stewardship, and public safety.
Accreditation Units
ENGG 130
★ 4.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-2)
Equilibrium of planar systems. Analysis of statically determinate trusses and frames. Friction. Centroids and centres of gravity. Forces and moments in beams. Second moments of area. Note: Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. Corequisite: MATH 100.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 50.4 Units
ENGL 199
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-0)
This course aims to develop the student's ability to provide effective written and oral information. It will focus on instruction in fundamental writing skills, including building effective sentences and paragraphs, and on learning to communicate clearly across a range of genres and media used in academic and professional contexts, including correspondence and presentations. Students will be introduced to the principles of information gathering, analysis, and citation. Note: Restricted to students in the Faculty of Engineering only.
Accreditation Units
MATH 100
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-1)
Review of numbers, inequalities, functions, analytic geometry; limits, continuity; derivatives and applications, Taylor polynomials; log, exp, and inverse trig functions. Integration, fundamental theorem of calculus substitution, trapezoidal and Simpson's rules. Prerequisites: Mathematics 30-1 and Mathematics 31. Notes: (1) Credit can be obtained in at most one of MATH 100, 113, 114, 117, 134, 144, 154, or SCI 100. (2) Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. (3) Restricted to Engineering students. Non-Engineering students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
PHYS 130
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-3/2)
Geometrical optics, optical instruments, oscillations, waves, sound, interference, diffraction. Prerequisites: Mathematics 30-1, Mathematics 31, Physics 30. Corequisite: MATH 100 or 113 or 114 or 117 or 134 or 144 or equivalent. Restricted to Engineering students. Other students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 47.2 Units
Winter Term 2
CHEM 105
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-3/2)
Rates of reactions, thermodynamics and equilibrium, electrochemistry, modern applications of chemistry. Prerequisite: CHEM 103 or 101. Note: Restricted to Engineering students only. Other students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 47.2 Units
ENCMP 100
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-1.5)
Fundamentals of computer programming with emphasis on solving engineering problems. Structure and syntax of computer programs, variables, data types, data structures, control structures, functions, input/output operations, debugging, software development process.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 21.3 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
ENGG 160
★ 2.0
(fi 4)(either term or Spring/Summer,
1-0-2)
Fundamental design process and theory in a multidisciplinary context. Importance, in engineering design, of communications; team work; the engineering disciplines, career fields; professional responsibilities of the engineer including elements of ethics, equity, concepts of sustainable development and environmental stewardship, public and worker safety and health considerations including the context of the Alberta Occupational Health and Safety Act. Corequisite ENGL 199. This course is delivered in a blended format.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 12.6 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 12.6 Units
EN PH 131
★ 4.3
(fi 6)(either term,
3-1s-3/2)
Kinematics and dynamics of particles; gravitation; work and energy; linear momentum; angular momentum; systems of particles; introduction to dynamics of rigid bodies. Prerequisites: MATH 100 or 117, and ENGG 130. Corequisite: MATH 101 or 118. Restricted to Engineering students. Other students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 26.8 Units
Engineering Science: 26.8 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 26.8 Units
MATH 101
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-1)
Area between curves, techniques of integration. Applications of integration to planar areas and lengths, volumes and masses. First order ordinary differential equations: separable, linear, direction fields, Euler's method, applications. Infinite series, power series, Taylor expansions with remainder terms. Polar coordinates. Rectangular, spherical and cylindrical coordinates in 3-dimensional space. Parametric curves in the plane and space: graphing, arc length, curvature; normal binormal, tangent plane in 3- dimensional space. Volumes and surface areas of rotation. Prerequisite: MATH 100. Notes: (1) Credit can be obtained in at most one of MATH 101, 115, 118, 136, 146, 156 or SCI 100. (2) Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. (3) Restricted to Engineering students. Non-Engineering students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
MATH 102
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-1)
Vectors and matrices, solution of linear equations, equations of lines and planes, determinants, matrix algebra, orthogonality and applications (Gram-Schmidt), eigenvalues and eigenvectors and applications, complex numbers. Prerequisite or corequisite: MATH 100. Notes: (1) Credit can be obtained in at most one of MATH 102, 125, or 127. (2) Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. (3) Restricted to Engineering students. Non-Engineering students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
Fall Term 3
ENGG 299
★ 1.5
(fi 2)(first term,
1-1s-0)
An examination of the history, philosophy and objectives of Cooperative Education; introduction to the operation of the Cooperative Education Program; self-assessment of transferable skills and work values; preparation of the resume; practice of job interview skills; goal setting on the job; ethics; human rights; and public and worker safety and health considerations including the context of the Alberta Occupational Health and Safety Act. Note: This course is only open to students registered in the Cooperative Education Program and must be taken prior to a student's first work placement.
Accreditation Units
MATH 201
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-0-1)
First-order equations; second-order linear equations: reduction of order, variation of parameters; Laplace transform; linear systems; power series; solution by series; separation of variables for PDEs. Prerequisite or corequisite: MATH 209 or 214. Notes: (1) Open only to students in Engineering, Specialization Physics, and Specialization Geophysics. (2) Credit can be obtained in at most one of MATH 201, MATH 334, MATH 336, or MA PH 251. (3) Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. Non-Engineering students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
MATH 209
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-1)
Partial differentiation, derivatives of integrals. Multiple integration using rectangular, cylindrical, and spherical coordinates. Vector Field Theory. Prerequisite: MATH 101. Prerequisite or corequisite: MATH 102. Notes: (1) This course may not be taken for credit if credit has already been obtained in MATH 215, MATH 315, MATH 317 or MA PH 351. (2) Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. (3) Restricted to Engineering students. Non-Engineering students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
MCTR 202
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Fall term,
3-0-3/2)
Circuit element definitions. Circuit laws: Ohm’s, KVL, KCL. Resistive voltage and current dividers. Basic loop and nodal analysis. Circuit theorems: linearity, Thevenin. Dependent sources. Time domain behavior of inductance and capacitance, energy storage. Sinusoidal signals, complex numbers, phasor and impedance concepts. Diodes: ideal and simple and models. Treatment of RLC circuits in the time domain, frequency domain and s-plane. Prerequisites: MATH 101, MATH 102.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.8 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 240
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Fall term,
3-0-1)
Introduction to linear systems and signal classification. Convolution. Fourier series expansion and Fourier transform (FT). Sampling and reconstruction. Discrete Fourier transform (DFT) and properties. Spectra analysis. Models of continuous-time systems and discrete-time systems for linear control system Z-transform and inverse Z-transform. Analysis of linear time invariant (LTI) systems. Design of linear time-invariant control systems. Corequisites: MCTR 202, MATH 201.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.8 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MEC E 230
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-1s-0)
Introduction to modes of heat transfer. One dimensional heat conduction. Heat transfer from surfaces. Introduction to fluid mechanics. Fluid properties. Fluid statics. Use of control volumes. Internal flows. Prerequisites: MATH 101, EN PH 131.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 11.0 Units
Engineering Science: 33.1 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 33.1 Units
MEC E 250
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-1s-0)
Moments of inertia. Kinematics and kinetics of rigid body motion, energy and momentum methods, impact, mechanical vibrations. Prerequisites: ENGG 130, EN PH 131 and MATH 101. There is a consolidated exam.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
Winter Term 4
CIV E 270
★ 4.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-0-3)
Plane stress and strain; stress-strain relationships; stresses and deformations resulting from axial and transverse loads; buckling of columns; torsion of circular sections; combined stress; statically indeterminate problems. Laboratory to demonstrate mechanical properties and verify assumptions of analysis. Prerequisites: ENGG 130 and MATH 101.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 56.7 Units
ECE 342
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-1s-0)
Deterministic and probabilistic models. Basics of probability theory: random experiments, axioms of probability, conditional probability and independence. Discrete and continuous random variables: cumulative distribution and probability density functions, functions of a random variable, expected values, transform methods. Pairs of random variables: independence, joint cdf and pdf, conditional probability and expectation, functions of a pair of random variables, jointly Gaussian random variables. Sums of random variables: the central limit theorem; basic types of random processes, wide sense stationary processes, autocorrelation and crosscorrelation, power spectrum, white noise. Prerequisite: MATH 209. Credit may be obtained in only one of ECE 342 or E E 387.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 19.8 Units
Engineering Science: 24.3 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 24.3 Units
MCTR 210
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-1)
Number systems, logic gates, Boolean algebra. Karnaugh maps. Combinational networks. State machines. Field programmable gate array (FPGA) implementation. Computer architecture. Assembly language. Addressing modes, subroutines, memory, input-output interfacing, and interrupts.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 260
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Winter Term,
2-0-3)
Design morphology, analysis and design of components, electro-mechanical system design and risk management concepts, design project aimed at assistive devices or technologies addressing user needs. Corequisite: MCTR 265.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 22.1 Units
Engineering Design: 22.1 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 22.1 Units
MCTR 265
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
2-0-3)
Computer-aided engineering, solid modelling, drafting and design. Introduction to multiphysics simulation. Design project aligned with MCTR 260.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.0 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
MCTR 294
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Fall term,
3-0-3/2)
Introduction to object-oriented programming for mechatronic applications. Introduction to data structures and classes with application to mechatronics. Introduction to algorithms. Concepts illustrated on a physical mechatronic system. Prerequisite: ENCMP 100.
Accreditation Units
Fall Term 5
MCTR 300
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Transistors, transistor amplifiers, and op-amp circuits; frequency response and filters; analog signal detection, conditioning, analysis, and conversion; transducers and electronic sensors for measuring common physical properties/phenomena. Understanding properties of signals in time and frequency domain; digitization of analog data; statistics, analysis, and uncertainty of measurement data. Prerequisites: MCTR 202, MCTR 240.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
MCTR 320
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Linear feedback control systems for command-following, stability, and dynamic response specifications. Frequency response and design techniques, including lead, lag compensators and PID control. An introduction to structural design limitations. Introduction to state space models. Examples emphasizing control of mechatronics systems, using computer-aided design. Prerequisite: MCTR 240. Credit can only be granted for one of MCTR 320, MEC E 420, ECE 360, CH E 446.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 53.5 Units
MCTR 350
★ 3.0
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-0)
Kinematics and dynamics of rigid bodies moving in three dimensions. Spatial kinematics of rigid bodies, Euler angles, tensor of inertia and the Newton-Euler equations of motion for rigid bodies, multi-body dynamics, inverse dynamics for manipulators. Prerequisite: MEC E 250.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 33.1 Units
Engineering Science: 11.0 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 11.0 Units
MCTR 355
★ 3.0
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-0)
Systems engineering definition, relevance, and benefits. The nature of technological systems and the concept of a system life cycle, from need to retirement. Requirements setting, including standards. Modelling system performance, with emphasis on mechatronic systems. System safety, risk, and reliability analysis. Ethical and sustainability considerations in systems design. Design for manufacturability and control. Design de-risking and testing for requirements compliance. Configuration management. Systems thinking and Indigenous perspectives.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science: 11.8 Units
Engineering Design: 23.6 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 35.4 Units
MCTR 357
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Coordinates systems, robot kinematics (forward and inverse), differential kinematics, robot dynamics, path and trajectory planning, position control, force control, impedance control, teleoperation systems.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 394
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Advanced topics in object-oriented programming for mechatronic applications. Advanced data structures, and algorithm analysis and design. Concepts illustrated using a physical mechatronic system and practical mechatronic applications. Introduction to modern robotic and mechatronic operating systems. Prerequisite: MCTR 294.
Accreditation Units
Spring/Summer Term 6
ECE 315
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-3/2)
Design and use of digital interfaces, including memory, serial, parallel, synchronous and asynchronous interfaces. Hardware implementations of interrupts, buses, input/output devices and direct memory access. Multitasking software architecture, real-time preemptive multitasking kernels. Data structures and mechanisms for flow control. Computer communications interfaces, interfacing of microcontroller to peripheral devices such as stepper motors. Requires payment of additional student instructional support fees. Refer to the Tuition and Fees page in the University Regulations section of the Calendar. Prerequisite: ECE 212 or E E 380 or CMPUT 229, and 275 or permission of the Instructor. Credit may be obtained in only one of CMPE 401 or ECE 315.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 21.3 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 332
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Spring/Summer,
3-0-3/2)
Force and torque generation in electric machines. AC and DC machines, permanent magnet synchronous (PMSM) and brushless DC motors (BLDC). Machine characteristics and dynamic models of electric actuators. Linear actuators; power electronics device characteristics; motor drives: H-bridges, inverters; speed control methods; power converters.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
MCTR 360
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Spring/Summer,
2-0-3)
A project-based course dealing with the design and implementation of a robotic system to accomplish a set of requirements. Integration of sensor technologies, sensor data processing, motion control based on feedback and real-time programming. Design procedures, ethics, safety and risk management, theory of engineering design, role of engineering analysis in design, application of computer-aided design software; component and material selection, codes, and standards; design optimization; system integration and verification through testing; teamwork, and a design project. Corequisite: MCTR 365.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 28.3 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 56.7 Units
MCTR 365
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Spring/Summer,
2-0-3)
Mechatronic and robotic system design using CAD tools. Concepts of function structure models, material selection, and introduction of load and stress analysis. Integration of sensors and actuators. Simulation of mechanisms, dynamics, kinematics, and heat transfer using commercial software. Emphasis is on numerical model design including testing and verification methods, and the critical interpretation of the computed results. Design project aligned with MCTR 360.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.0 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
MCTR 370
★ 3.0
(fi 6.0)(Spring/Summer,
3-0-0)
Fundamentals of machine learning methods. Supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning concepts, and fundamentals of fuzzy logic. Review of probability and optimization. Linear regression. Linear classification and logistic regression. Components of modern machine learning approaches, including feature engineering, neural network models, training and evaluation methodology, and deep learning libraries. Object detection and object/human pose regression for robotic applications. Bias in machine learning algorithms. Corequisite: MCTR 399.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.8 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 399
★ 3.0
(fi 6.0)(Spring/Summer,
3-0-0)
Analytical and numerical methods with mechatronics applications. Complex numbers, partial differential equations, analytic functions, elementary functions, mappings, integrals, series, residues and poles, integral formulas. Statistical tests. Numerical integration and differentiation, solution methods of boundary value problems. Use of programming languages to implement numerical methods. Critical-thinking applied to problems related to mechatronics systems. Formulation, methodologies, and techniques for numerical solutions of engineering issues, particularly those arising within the field of mechatronics.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
Fall Term 7
Complementary Elective
A complementary elective of the student's choice. Please consult the calendar for more information.
ENG M 401
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-0)
The application of the fundamentals of engineering economics, financial analysis and market assessment to engineering alternatives in the planning, development and ongoing management of industrial enterprises. The course covers the use of engineering, economic, financial and market assessment information in investment and business operation decisions in technology oriented companies. Note: Credit cannot be obtained for more than one of ENGG 310, ENGG 401, ENG M 310, or ENG M 401.
Accreditation Units
Program/Technical Elective
A program/technical elective of the student's choice. Please consult the calendar for more information.
Program/Technical Elective
A program/technical elective of the student's choice. Please consult the calendar for more information.
MCTR 420
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Fall term,
3-0-3/2)
System states and state space models. Linearization of nonlinear state-space models. Solving linear time-invariant state-space equations. Controllability and observability, and their algebraic tests. Minimal state-space realizations. State feedback and eigenvalue/pole assignment. Step tracking control design. State estimation and observer design. Observer-based control. Introduction to linear quadratic optimal control. Prerequisite: MCTR 320.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 460
★ 2.5
(fi 6.0)(Fall term,
1-0-3)
PART 1: Feasibility study and detailed design of a project which requires students to exercise creative ability, to make assumptions and decisions based on synthesis of technical knowledge, and devise new designs. Advanced design safety review.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 56.7 Units
Winter Term 8
ITS Elective
An ITS elective of the student's choice. Please consult the calendar for more information.
ENGG 400
★ 1.0
(fi 2)(either term,
1-0-0)
The technical and professional duties and responsibilities of the engineer; the ethics of the engineering profession; technical and professional organizations. The role of the engineer in the social environment including elements of equity, concepts of sustainable development and environmental stewardship, public and worker safety and health considerations including the context of the Alberta Occupational Health and Safety Act. Note: Restricted to fourth-year traditional and fifth-year co-op engineering students. Must be taken in last term of program.
Accreditation Units
MCTR 421
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Review of probability, random variables, and stochastic processes. Recursive state estimation: Bayes filter, linear Kalman filter and its extension to nonlinear systems. Practical applications of filtering techniques to mechatronics systems. Prerequisite: MCTR 420.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.8 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 461
★ 2.5
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
1-0-3)
PART 2: Feasibility study and detailed design of a project which requires students to exercise creative ability, to make assumptions and decisions based on synthesis of technical knowledge, and devise new designs. Advanced design safety review. Prerequisite: MCTR 460.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 56.7 Units
MCTR 465
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Introduction to mobile robots. Means of locomotion and kinematic and dynamic models. Linear and nonlinear motion control theory and filtering applied mobile robots. Map-based and reactive motion planning. Localization and mapping. Visual servoing. Prerequisite: MCTR 394. Corequisite: MCTR 421.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 35.4 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
Program/Technical Elective
A program/technical elective of the student's choice. Please consult the calendar for more information.
Fall Term 1
CHEM 103
★ 4.3
(fi 6)(either term,
3-1s-3/2)
Atoms and molecules, states of matter, chemistry of the elements. Prerequisite: Chemistry 30, or equivalent. Note: Restricted to Engineering students only. Other students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 53.5 Units
ENGG 100
★ 1.1
(fi 2)(either term,
.75-.75s-0)
An introduction to the Faculty of Engineering, the engineering profession, the skills required for academic success, and the fundamentals of leadership: study and life skills; time management and goal setting; interpersonal skills; career planning; engineering and society including elements of ethics, equity, concepts of sustainable development, environmental stewardship, and public safety.
Accreditation Units
ENGG 130
★ 4.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-2)
Equilibrium of planar systems. Analysis of statically determinate trusses and frames. Friction. Centroids and centres of gravity. Forces and moments in beams. Second moments of area. Note: Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. Corequisite: MATH 100.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 50.4 Units
ENGL 199
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-0)
This course aims to develop the student's ability to provide effective written and oral information. It will focus on instruction in fundamental writing skills, including building effective sentences and paragraphs, and on learning to communicate clearly across a range of genres and media used in academic and professional contexts, including correspondence and presentations. Students will be introduced to the principles of information gathering, analysis, and citation. Note: Restricted to students in the Faculty of Engineering only.
Accreditation Units
MATH 100
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-1)
Review of numbers, inequalities, functions, analytic geometry; limits, continuity; derivatives and applications, Taylor polynomials; log, exp, and inverse trig functions. Integration, fundamental theorem of calculus substitution, trapezoidal and Simpson's rules. Prerequisites: Mathematics 30-1 and Mathematics 31. Notes: (1) Credit can be obtained in at most one of MATH 100, 113, 114, 117, 134, 144, 154, or SCI 100. (2) Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. (3) Restricted to Engineering students. Non-Engineering students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
PHYS 130
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-3/2)
Geometrical optics, optical instruments, oscillations, waves, sound, interference, diffraction. Prerequisites: Mathematics 30-1, Mathematics 31, Physics 30. Corequisite: MATH 100 or 113 or 114 or 117 or 134 or 144 or equivalent. Restricted to Engineering students. Other students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 47.2 Units
Winter Term 2
CHEM 105
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-3/2)
Rates of reactions, thermodynamics and equilibrium, electrochemistry, modern applications of chemistry. Prerequisite: CHEM 103 or 101. Note: Restricted to Engineering students only. Other students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 47.2 Units
ENCMP 100
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-1.5)
Fundamentals of computer programming with emphasis on solving engineering problems. Structure and syntax of computer programs, variables, data types, data structures, control structures, functions, input/output operations, debugging, software development process.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 21.3 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
ENGG 160
★ 2.0
(fi 4)(either term or Spring/Summer,
1-0-2)
Fundamental design process and theory in a multidisciplinary context. Importance, in engineering design, of communications; team work; the engineering disciplines, career fields; professional responsibilities of the engineer including elements of ethics, equity, concepts of sustainable development and environmental stewardship, public and worker safety and health considerations including the context of the Alberta Occupational Health and Safety Act. Corequisite ENGL 199. This course is delivered in a blended format.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 12.6 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 12.6 Units
EN PH 131
★ 4.3
(fi 6)(either term,
3-1s-3/2)
Kinematics and dynamics of particles; gravitation; work and energy; linear momentum; angular momentum; systems of particles; introduction to dynamics of rigid bodies. Prerequisites: MATH 100 or 117, and ENGG 130. Corequisite: MATH 101 or 118. Restricted to Engineering students. Other students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 26.8 Units
Engineering Science: 26.8 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 26.8 Units
MATH 101
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-1)
Area between curves, techniques of integration. Applications of integration to planar areas and lengths, volumes and masses. First order ordinary differential equations: separable, linear, direction fields, Euler's method, applications. Infinite series, power series, Taylor expansions with remainder terms. Polar coordinates. Rectangular, spherical and cylindrical coordinates in 3-dimensional space. Parametric curves in the plane and space: graphing, arc length, curvature; normal binormal, tangent plane in 3- dimensional space. Volumes and surface areas of rotation. Prerequisite: MATH 100. Notes: (1) Credit can be obtained in at most one of MATH 101, 115, 118, 136, 146, 156 or SCI 100. (2) Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. (3) Restricted to Engineering students. Non-Engineering students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
MATH 102
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-1)
Vectors and matrices, solution of linear equations, equations of lines and planes, determinants, matrix algebra, orthogonality and applications (Gram-Schmidt), eigenvalues and eigenvectors and applications, complex numbers. Prerequisite or corequisite: MATH 100. Notes: (1) Credit can be obtained in at most one of MATH 102, 125, or 127. (2) Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. (3) Restricted to Engineering students. Non-Engineering students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
Fall Term 3
ENGG 299
★ 1.5
(fi 2)(first term,
1-1s-0)
An examination of the history, philosophy and objectives of Cooperative Education; introduction to the operation of the Cooperative Education Program; self-assessment of transferable skills and work values; preparation of the resume; practice of job interview skills; goal setting on the job; ethics; human rights; and public and worker safety and health considerations including the context of the Alberta Occupational Health and Safety Act. Note: This course is only open to students registered in the Cooperative Education Program and must be taken prior to a student's first work placement.
Accreditation Units
MATH 201
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-0-1)
First-order equations; second-order linear equations: reduction of order, variation of parameters; Laplace transform; linear systems; power series; solution by series; separation of variables for PDEs. Prerequisite or corequisite: MATH 209 or 214. Notes: (1) Open only to students in Engineering, Specialization Physics, and Specialization Geophysics. (2) Credit can be obtained in at most one of MATH 201, MATH 334, MATH 336, or MA PH 251. (3) Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. Non-Engineering students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
MATH 209
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-1)
Partial differentiation, derivatives of integrals. Multiple integration using rectangular, cylindrical, and spherical coordinates. Vector Field Theory. Prerequisite: MATH 101. Prerequisite or corequisite: MATH 102. Notes: (1) This course may not be taken for credit if credit has already been obtained in MATH 215, MATH 315, MATH 317 or MA PH 351. (2) Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. (3) Restricted to Engineering students. Non-Engineering students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
MCTR 202
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Fall term,
3-0-3/2)
Circuit element definitions. Circuit laws: Ohm’s, KVL, KCL. Resistive voltage and current dividers. Basic loop and nodal analysis. Circuit theorems: linearity, Thevenin. Dependent sources. Time domain behavior of inductance and capacitance, energy storage. Sinusoidal signals, complex numbers, phasor and impedance concepts. Diodes: ideal and simple and models. Treatment of RLC circuits in the time domain, frequency domain and s-plane. Prerequisites: MATH 101, MATH 102.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.8 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 240
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Fall term,
3-0-1)
Introduction to linear systems and signal classification. Convolution. Fourier series expansion and Fourier transform (FT). Sampling and reconstruction. Discrete Fourier transform (DFT) and properties. Spectra analysis. Models of continuous-time systems and discrete-time systems for linear control system Z-transform and inverse Z-transform. Analysis of linear time invariant (LTI) systems. Design of linear time-invariant control systems. Corequisites: MCTR 202, MATH 201.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.8 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MEC E 230
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-1s-0)
Introduction to modes of heat transfer. One dimensional heat conduction. Heat transfer from surfaces. Introduction to fluid mechanics. Fluid properties. Fluid statics. Use of control volumes. Internal flows. Prerequisites: MATH 101, EN PH 131.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 11.0 Units
Engineering Science: 33.1 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 33.1 Units
MEC E 250
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-1s-0)
Moments of inertia. Kinematics and kinetics of rigid body motion, energy and momentum methods, impact, mechanical vibrations. Prerequisites: ENGG 130, EN PH 131 and MATH 101. There is a consolidated exam.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
Winter Term 4
CIV E 270
★ 4.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-0-3)
Plane stress and strain; stress-strain relationships; stresses and deformations resulting from axial and transverse loads; buckling of columns; torsion of circular sections; combined stress; statically indeterminate problems. Laboratory to demonstrate mechanical properties and verify assumptions of analysis. Prerequisites: ENGG 130 and MATH 101.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 56.7 Units
ECE 342
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-1s-0)
Deterministic and probabilistic models. Basics of probability theory: random experiments, axioms of probability, conditional probability and independence. Discrete and continuous random variables: cumulative distribution and probability density functions, functions of a random variable, expected values, transform methods. Pairs of random variables: independence, joint cdf and pdf, conditional probability and expectation, functions of a pair of random variables, jointly Gaussian random variables. Sums of random variables: the central limit theorem; basic types of random processes, wide sense stationary processes, autocorrelation and crosscorrelation, power spectrum, white noise. Prerequisite: MATH 209. Credit may be obtained in only one of ECE 342 or E E 387.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 19.8 Units
Engineering Science: 24.3 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 24.3 Units
MCTR 210
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-1)
Number systems, logic gates, Boolean algebra. Karnaugh maps. Combinational networks. State machines. Field programmable gate array (FPGA) implementation. Computer architecture. Assembly language. Addressing modes, subroutines, memory, input-output interfacing, and interrupts.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 260
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Winter Term,
2-0-3)
Design morphology, analysis and design of components, electro-mechanical system design and risk management concepts, design project aimed at assistive devices or technologies addressing user needs. Corequisite: MCTR 265.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 22.1 Units
Engineering Design: 22.1 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 22.1 Units
MCTR 265
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
2-0-3)
Computer-aided engineering, solid modelling, drafting and design. Introduction to multiphysics simulation. Design project aligned with MCTR 260.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.0 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
MCTR 294
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Fall term,
3-0-3/2)
Introduction to object-oriented programming for mechatronic applications. Introduction to data structures and classes with application to mechatronics. Introduction to algorithms. Concepts illustrated on a physical mechatronic system. Prerequisite: ENCMP 100.
Accreditation Units
Summer Co-op Term 1
WKEXP 901
★ 0.5
(fi 7)(either term or Spring/Summer,
unassigned)
A four-month work placement for Engineering students registered in the Cooperative Education Program. This work experience will provide the student with exposure to the practical application of engineering and the general work environment. Evaluation will be based on the employer's performance appraisal, the student's work term report, and the student's ability to learn from the experiences of the work term. Prerequisite: ENGG 299.
Accreditation Units
Fall Co-op Term 2
WKEXP 902
★ 0.5
(fi 7)(either term or Spring/Summer,
unassigned)
A four-month work placement for Engineering students registered in the Cooperative Education Program. This work experience will provide the student with exposure to the practical application of engineering and the general work environment. Evaluation will be based on the employer's performance appraisal, the student's work term report, and the student's ability to learn from the experiences of the work term. Prerequisite: WKEXP 901.
Accreditation Units
Winter Term 5
MCTR 300
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Transistors, transistor amplifiers, and op-amp circuits; frequency response and filters; analog signal detection, conditioning, analysis, and conversion; transducers and electronic sensors for measuring common physical properties/phenomena. Understanding properties of signals in time and frequency domain; digitization of analog data; statistics, analysis, and uncertainty of measurement data. Prerequisites: MCTR 202, MCTR 240.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
MCTR 320
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Linear feedback control systems for command-following, stability, and dynamic response specifications. Frequency response and design techniques, including lead, lag compensators and PID control. An introduction to structural design limitations. Introduction to state space models. Examples emphasizing control of mechatronics systems, using computer-aided design. Prerequisite: MCTR 240. Credit can only be granted for one of MCTR 320, MEC E 420, ECE 360, CH E 446.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 53.5 Units
MCTR 350
★ 3.0
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-0)
Kinematics and dynamics of rigid bodies moving in three dimensions. Spatial kinematics of rigid bodies, Euler angles, tensor of inertia and the Newton-Euler equations of motion for rigid bodies, multi-body dynamics, inverse dynamics for manipulators. Prerequisite: MEC E 250.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 33.1 Units
Engineering Science: 11.0 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 11.0 Units
MCTR 355
★ 3.0
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-0)
Systems engineering definition, relevance, and benefits. The nature of technological systems and the concept of a system life cycle, from need to retirement. Requirements setting, including standards. Modelling system performance, with emphasis on mechatronic systems. System safety, risk, and reliability analysis. Ethical and sustainability considerations in systems design. Design for manufacturability and control. Design de-risking and testing for requirements compliance. Configuration management. Systems thinking and Indigenous perspectives.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science: 11.8 Units
Engineering Design: 23.6 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 35.4 Units
MCTR 357
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Coordinates systems, robot kinematics (forward and inverse), differential kinematics, robot dynamics, path and trajectory planning, position control, force control, impedance control, teleoperation systems.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 394
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Advanced topics in object-oriented programming for mechatronic applications. Advanced data structures, and algorithm analysis and design. Concepts illustrated using a physical mechatronic system and practical mechatronic applications. Introduction to modern robotic and mechatronic operating systems. Prerequisite: MCTR 294.
Accreditation Units
Summer Term 6
ECE 315
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-3/2)
Design and use of digital interfaces, including memory, serial, parallel, synchronous and asynchronous interfaces. Hardware implementations of interrupts, buses, input/output devices and direct memory access. Multitasking software architecture, real-time preemptive multitasking kernels. Data structures and mechanisms for flow control. Computer communications interfaces, interfacing of microcontroller to peripheral devices such as stepper motors. Requires payment of additional student instructional support fees. Refer to the Tuition and Fees page in the University Regulations section of the Calendar. Prerequisite: ECE 212 or E E 380 or CMPUT 229, and 275 or permission of the Instructor. Credit may be obtained in only one of CMPE 401 or ECE 315.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 21.3 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 332
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Spring/Summer,
3-0-3/2)
Force and torque generation in electric machines. AC and DC machines, permanent magnet synchronous (PMSM) and brushless DC motors (BLDC). Machine characteristics and dynamic models of electric actuators. Linear actuators; power electronics device characteristics; motor drives: H-bridges, inverters; speed control methods; power converters.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
MCTR 360
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Spring/Summer,
2-0-3)
A project-based course dealing with the design and implementation of a robotic system to accomplish a set of requirements. Integration of sensor technologies, sensor data processing, motion control based on feedback and real-time programming. Design procedures, ethics, safety and risk management, theory of engineering design, role of engineering analysis in design, application of computer-aided design software; component and material selection, codes, and standards; design optimization; system integration and verification through testing; teamwork, and a design project. Corequisite: MCTR 365.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 28.3 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 56.7 Units
MCTR 365
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Spring/Summer,
2-0-3)
Mechatronic and robotic system design using CAD tools. Concepts of function structure models, material selection, and introduction of load and stress analysis. Integration of sensors and actuators. Simulation of mechanisms, dynamics, kinematics, and heat transfer using commercial software. Emphasis is on numerical model design including testing and verification methods, and the critical interpretation of the computed results. Design project aligned with MCTR 360.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.0 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
MCTR 370
★ 3.0
(fi 6.0)(Spring/Summer,
3-0-0)
Fundamentals of machine learning methods. Supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning concepts, and fundamentals of fuzzy logic. Review of probability and optimization. Linear regression. Linear classification and logistic regression. Components of modern machine learning approaches, including feature engineering, neural network models, training and evaluation methodology, and deep learning libraries. Object detection and object/human pose regression for robotic applications. Bias in machine learning algorithms. Corequisite: MCTR 399.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.8 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 399
★ 3.0
(fi 6.0)(Spring/Summer,
3-0-0)
Analytical and numerical methods with mechatronics applications. Complex numbers, partial differential equations, analytic functions, elementary functions, mappings, integrals, series, residues and poles, integral formulas. Statistical tests. Numerical integration and differentiation, solution methods of boundary value problems. Use of programming languages to implement numerical methods. Critical-thinking applied to problems related to mechatronics systems. Formulation, methodologies, and techniques for numerical solutions of engineering issues, particularly those arising within the field of mechatronics.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
Fall Co-op Term 3
WKEXP 903
★ 0.5
(fi 7)(either term or Spring/Summer,
unassigned)
A four-month work placement for Engineering students registered in the Cooperative Education Program. This work experience will provide students with personal involvement in the practice of their engineering discipline commensurate with their level of academic preparation. Evaluation will be based on the employer's performance appraisal, the student's work term report, and the student's ability to learn from the experiences of the work term. Prerequisite: WKEXP 902.
Accreditation Units
Winter Co-op Term 4
WKEXP 904
★ 0.5
(fi 7)(either term or Spring/Summer,
unassigned)
A four-month work placement for Engineering students registered in the Cooperative Education Program. This work experience will provide students with personal involvement in the practice of their engineering discipline commensurate with their level of academic preparation. Evaluation will be based on the employer's performance appraisal, the student's work term report, and the student's ability to learn from the experiences of the work term. Prerequisite: WKEXP 903.
Accreditation Units
Summer Co-op Term 5
WKEXP 905
★ 3.0
(fi 7)(either term or Spring/Summer,
unassigned)
A four-month work placement for Engineering students registered in the Cooperative Education Program. This work experience will provide students with personal involvement in the practice of their engineering discipline commensurate with their level of academic preparation. Evaluation will be based on the employer's performance appraisal, the student's work term report, and the student's ability to learn from the experiences of the work term. Prerequisite: WKEXP 904.
Accreditation Units
Fall Term 7
Complementary Elective
A complementary elective of the student's choice. Please consult the calendar for more information.
ENG M 401
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-0)
The application of the fundamentals of engineering economics, financial analysis and market assessment to engineering alternatives in the planning, development and ongoing management of industrial enterprises. The course covers the use of engineering, economic, financial and market assessment information in investment and business operation decisions in technology oriented companies. Note: Credit cannot be obtained for more than one of ENGG 310, ENGG 401, ENG M 310, or ENG M 401.
Accreditation Units
Program/Technical Elective
A program/technical elective of the student's choice. Please consult the calendar for more information.
Program/Technical Elective
A program/technical elective of the student's choice. Please consult the calendar for more information.
MCTR 420
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Fall term,
3-0-3/2)
System states and state space models. Linearization of nonlinear state-space models. Solving linear time-invariant state-space equations. Controllability and observability, and their algebraic tests. Minimal state-space realizations. State feedback and eigenvalue/pole assignment. Step tracking control design. State estimation and observer design. Observer-based control. Introduction to linear quadratic optimal control. Prerequisite: MCTR 320.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 460
★ 2.5
(fi 6.0)(Fall term,
1-0-3)
PART 1: Feasibility study and detailed design of a project which requires students to exercise creative ability, to make assumptions and decisions based on synthesis of technical knowledge, and devise new designs. Advanced design safety review.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 56.7 Units
Winter Term 8
ITS Elective
An ITS elective of the student's choice. Please consult the calendar for more information.
ENGG 400
★ 1.0
(fi 2)(either term,
1-0-0)
The technical and professional duties and responsibilities of the engineer; the ethics of the engineering profession; technical and professional organizations. The role of the engineer in the social environment including elements of equity, concepts of sustainable development and environmental stewardship, public and worker safety and health considerations including the context of the Alberta Occupational Health and Safety Act. Note: Restricted to fourth-year traditional and fifth-year co-op engineering students. Must be taken in last term of program.
Accreditation Units
MCTR 421
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Review of probability, random variables, and stochastic processes. Recursive state estimation: Bayes filter, linear Kalman filter and its extension to nonlinear systems. Practical applications of filtering techniques to mechatronics systems. Prerequisite: MCTR 420.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.8 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 461
★ 2.5
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
1-0-3)
PART 2: Feasibility study and detailed design of a project which requires students to exercise creative ability, to make assumptions and decisions based on synthesis of technical knowledge, and devise new designs. Advanced design safety review. Prerequisite: MCTR 460.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 56.7 Units
MCTR 465
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Introduction to mobile robots. Means of locomotion and kinematic and dynamic models. Linear and nonlinear motion control theory and filtering applied mobile robots. Map-based and reactive motion planning. Localization and mapping. Visual servoing. Prerequisite: MCTR 394. Corequisite: MCTR 421.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 35.4 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
Program/Technical Elective
A program/technical elective of the student's choice. Please consult the calendar for more information.
Fall Term 1
CHEM 103
★ 4.3
(fi 6)(either term,
3-1s-3/2)
Atoms and molecules, states of matter, chemistry of the elements. Prerequisite: Chemistry 30, or equivalent. Note: Restricted to Engineering students only. Other students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 53.5 Units
ENGG 100
★ 1.1
(fi 2)(either term,
.75-.75s-0)
An introduction to the Faculty of Engineering, the engineering profession, the skills required for academic success, and the fundamentals of leadership: study and life skills; time management and goal setting; interpersonal skills; career planning; engineering and society including elements of ethics, equity, concepts of sustainable development, environmental stewardship, and public safety.
Accreditation Units
ENGG 130
★ 4.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-2)
Equilibrium of planar systems. Analysis of statically determinate trusses and frames. Friction. Centroids and centres of gravity. Forces and moments in beams. Second moments of area. Note: Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. Corequisite: MATH 100.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 50.4 Units
ENGL 199
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-0)
This course aims to develop the student's ability to provide effective written and oral information. It will focus on instruction in fundamental writing skills, including building effective sentences and paragraphs, and on learning to communicate clearly across a range of genres and media used in academic and professional contexts, including correspondence and presentations. Students will be introduced to the principles of information gathering, analysis, and citation. Note: Restricted to students in the Faculty of Engineering only.
Accreditation Units
MATH 100
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-1)
Review of numbers, inequalities, functions, analytic geometry; limits, continuity; derivatives and applications, Taylor polynomials; log, exp, and inverse trig functions. Integration, fundamental theorem of calculus substitution, trapezoidal and Simpson's rules. Prerequisites: Mathematics 30-1 and Mathematics 31. Notes: (1) Credit can be obtained in at most one of MATH 100, 113, 114, 117, 134, 144, 154, or SCI 100. (2) Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. (3) Restricted to Engineering students. Non-Engineering students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
PHYS 130
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-3/2)
Geometrical optics, optical instruments, oscillations, waves, sound, interference, diffraction. Prerequisites: Mathematics 30-1, Mathematics 31, Physics 30. Corequisite: MATH 100 or 113 or 114 or 117 or 134 or 144 or equivalent. Restricted to Engineering students. Other students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 47.2 Units
Winter Term 2
CHEM 105
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-3/2)
Rates of reactions, thermodynamics and equilibrium, electrochemistry, modern applications of chemistry. Prerequisite: CHEM 103 or 101. Note: Restricted to Engineering students only. Other students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 47.2 Units
ENCMP 100
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-1.5)
Fundamentals of computer programming with emphasis on solving engineering problems. Structure and syntax of computer programs, variables, data types, data structures, control structures, functions, input/output operations, debugging, software development process.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 21.3 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
ENGG 160
★ 2.0
(fi 4)(either term or Spring/Summer,
1-0-2)
Fundamental design process and theory in a multidisciplinary context. Importance, in engineering design, of communications; team work; the engineering disciplines, career fields; professional responsibilities of the engineer including elements of ethics, equity, concepts of sustainable development and environmental stewardship, public and worker safety and health considerations including the context of the Alberta Occupational Health and Safety Act. Corequisite ENGL 199. This course is delivered in a blended format.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 12.6 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 12.6 Units
EN PH 131
★ 4.3
(fi 6)(either term,
3-1s-3/2)
Kinematics and dynamics of particles; gravitation; work and energy; linear momentum; angular momentum; systems of particles; introduction to dynamics of rigid bodies. Prerequisites: MATH 100 or 117, and ENGG 130. Corequisite: MATH 101 or 118. Restricted to Engineering students. Other students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 26.8 Units
Engineering Science: 26.8 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 26.8 Units
MATH 101
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-1)
Area between curves, techniques of integration. Applications of integration to planar areas and lengths, volumes and masses. First order ordinary differential equations: separable, linear, direction fields, Euler's method, applications. Infinite series, power series, Taylor expansions with remainder terms. Polar coordinates. Rectangular, spherical and cylindrical coordinates in 3-dimensional space. Parametric curves in the plane and space: graphing, arc length, curvature; normal binormal, tangent plane in 3- dimensional space. Volumes and surface areas of rotation. Prerequisite: MATH 100. Notes: (1) Credit can be obtained in at most one of MATH 101, 115, 118, 136, 146, 156 or SCI 100. (2) Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. (3) Restricted to Engineering students. Non-Engineering students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
MATH 102
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-1)
Vectors and matrices, solution of linear equations, equations of lines and planes, determinants, matrix algebra, orthogonality and applications (Gram-Schmidt), eigenvalues and eigenvectors and applications, complex numbers. Prerequisite or corequisite: MATH 100. Notes: (1) Credit can be obtained in at most one of MATH 102, 125, or 127. (2) Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. (3) Restricted to Engineering students. Non-Engineering students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
Fall Term 3
ENGG 299
★ 1.5
(fi 2)(first term,
1-1s-0)
An examination of the history, philosophy and objectives of Cooperative Education; introduction to the operation of the Cooperative Education Program; self-assessment of transferable skills and work values; preparation of the resume; practice of job interview skills; goal setting on the job; ethics; human rights; and public and worker safety and health considerations including the context of the Alberta Occupational Health and Safety Act. Note: This course is only open to students registered in the Cooperative Education Program and must be taken prior to a student's first work placement.
Accreditation Units
MATH 201
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-0-1)
First-order equations; second-order linear equations: reduction of order, variation of parameters; Laplace transform; linear systems; power series; solution by series; separation of variables for PDEs. Prerequisite or corequisite: MATH 209 or 214. Notes: (1) Open only to students in Engineering, Specialization Physics, and Specialization Geophysics. (2) Credit can be obtained in at most one of MATH 201, MATH 334, MATH 336, or MA PH 251. (3) Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. Non-Engineering students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
MATH 209
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-1)
Partial differentiation, derivatives of integrals. Multiple integration using rectangular, cylindrical, and spherical coordinates. Vector Field Theory. Prerequisite: MATH 101. Prerequisite or corequisite: MATH 102. Notes: (1) This course may not be taken for credit if credit has already been obtained in MATH 215, MATH 315, MATH 317 or MA PH 351. (2) Students in all sections of this course will write a common final examination. (3) Restricted to Engineering students. Non-Engineering students who take this course will receive 3 units.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
MCTR 202
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Fall term,
3-0-3/2)
Circuit element definitions. Circuit laws: Ohm’s, KVL, KCL. Resistive voltage and current dividers. Basic loop and nodal analysis. Circuit theorems: linearity, Thevenin. Dependent sources. Time domain behavior of inductance and capacitance, energy storage. Sinusoidal signals, complex numbers, phasor and impedance concepts. Diodes: ideal and simple and models. Treatment of RLC circuits in the time domain, frequency domain and s-plane. Prerequisites: MATH 101, MATH 102.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.8 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 240
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Fall term,
3-0-1)
Introduction to linear systems and signal classification. Convolution. Fourier series expansion and Fourier transform (FT). Sampling and reconstruction. Discrete Fourier transform (DFT) and properties. Spectra analysis. Models of continuous-time systems and discrete-time systems for linear control system Z-transform and inverse Z-transform. Analysis of linear time invariant (LTI) systems. Design of linear time-invariant control systems. Corequisites: MCTR 202, MATH 201.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.8 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MEC E 230
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-1s-0)
Introduction to modes of heat transfer. One dimensional heat conduction. Heat transfer from surfaces. Introduction to fluid mechanics. Fluid properties. Fluid statics. Use of control volumes. Internal flows. Prerequisites: MATH 101, EN PH 131.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 11.0 Units
Engineering Science: 33.1 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 33.1 Units
MEC E 250
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-1s-0)
Moments of inertia. Kinematics and kinetics of rigid body motion, energy and momentum methods, impact, mechanical vibrations. Prerequisites: ENGG 130, EN PH 131 and MATH 101. There is a consolidated exam.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
Winter Term 4
CIV E 270
★ 4.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-0-3)
Plane stress and strain; stress-strain relationships; stresses and deformations resulting from axial and transverse loads; buckling of columns; torsion of circular sections; combined stress; statically indeterminate problems. Laboratory to demonstrate mechanical properties and verify assumptions of analysis. Prerequisites: ENGG 130 and MATH 101.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 56.7 Units
ECE 342
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-1s-0)
Deterministic and probabilistic models. Basics of probability theory: random experiments, axioms of probability, conditional probability and independence. Discrete and continuous random variables: cumulative distribution and probability density functions, functions of a random variable, expected values, transform methods. Pairs of random variables: independence, joint cdf and pdf, conditional probability and expectation, functions of a pair of random variables, jointly Gaussian random variables. Sums of random variables: the central limit theorem; basic types of random processes, wide sense stationary processes, autocorrelation and crosscorrelation, power spectrum, white noise. Prerequisite: MATH 209. Credit may be obtained in only one of ECE 342 or E E 387.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 19.8 Units
Engineering Science: 24.3 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 24.3 Units
MCTR 210
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-1)
Number systems, logic gates, Boolean algebra. Karnaugh maps. Combinational networks. State machines. Field programmable gate array (FPGA) implementation. Computer architecture. Assembly language. Addressing modes, subroutines, memory, input-output interfacing, and interrupts.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 260
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Winter Term,
2-0-3)
Design morphology, analysis and design of components, electro-mechanical system design and risk management concepts, design project aimed at assistive devices or technologies addressing user needs. Corequisite: MCTR 265.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 22.1 Units
Engineering Design: 22.1 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 22.1 Units
MCTR 265
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
2-0-3)
Computer-aided engineering, solid modelling, drafting and design. Introduction to multiphysics simulation. Design project aligned with MCTR 260.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.0 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
MCTR 294
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Fall term,
3-0-3/2)
Introduction to object-oriented programming for mechatronic applications. Introduction to data structures and classes with application to mechatronics. Introduction to algorithms. Concepts illustrated on a physical mechatronic system. Prerequisite: ENCMP 100.
Accreditation Units
Fall Term 5
MCTR 300
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Transistors, transistor amplifiers, and op-amp circuits; frequency response and filters; analog signal detection, conditioning, analysis, and conversion; transducers and electronic sensors for measuring common physical properties/phenomena. Understanding properties of signals in time and frequency domain; digitization of analog data; statistics, analysis, and uncertainty of measurement data. Prerequisites: MCTR 202, MCTR 240.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
MCTR 320
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Linear feedback control systems for command-following, stability, and dynamic response specifications. Frequency response and design techniques, including lead, lag compensators and PID control. An introduction to structural design limitations. Introduction to state space models. Examples emphasizing control of mechatronics systems, using computer-aided design. Prerequisite: MCTR 240. Credit can only be granted for one of MCTR 320, MEC E 420, ECE 360, CH E 446.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 53.5 Units
MCTR 350
★ 3.0
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-0)
Kinematics and dynamics of rigid bodies moving in three dimensions. Spatial kinematics of rigid bodies, Euler angles, tensor of inertia and the Newton-Euler equations of motion for rigid bodies, multi-body dynamics, inverse dynamics for manipulators. Prerequisite: MEC E 250.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 33.1 Units
Engineering Science: 11.0 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 11.0 Units
MCTR 355
★ 3.0
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-0)
Systems engineering definition, relevance, and benefits. The nature of technological systems and the concept of a system life cycle, from need to retirement. Requirements setting, including standards. Modelling system performance, with emphasis on mechatronic systems. System safety, risk, and reliability analysis. Ethical and sustainability considerations in systems design. Design for manufacturability and control. Design de-risking and testing for requirements compliance. Configuration management. Systems thinking and Indigenous perspectives.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science: 11.8 Units
Engineering Design: 23.6 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 35.4 Units
MCTR 357
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Coordinates systems, robot kinematics (forward and inverse), differential kinematics, robot dynamics, path and trajectory planning, position control, force control, impedance control, teleoperation systems.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 394
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Advanced topics in object-oriented programming for mechatronic applications. Advanced data structures, and algorithm analysis and design. Concepts illustrated using a physical mechatronic system and practical mechatronic applications. Introduction to modern robotic and mechatronic operating systems. Prerequisite: MCTR 294.
Accreditation Units
Winter Term 6
ECE 315
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-3/2)
Design and use of digital interfaces, including memory, serial, parallel, synchronous and asynchronous interfaces. Hardware implementations of interrupts, buses, input/output devices and direct memory access. Multitasking software architecture, real-time preemptive multitasking kernels. Data structures and mechanisms for flow control. Computer communications interfaces, interfacing of microcontroller to peripheral devices such as stepper motors. Requires payment of additional student instructional support fees. Refer to the Tuition and Fees page in the University Regulations section of the Calendar. Prerequisite: ECE 212 or E E 380 or CMPUT 229, and 275 or permission of the Instructor. Credit may be obtained in only one of CMPE 401 or ECE 315.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 21.3 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 332
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Spring/Summer,
3-0-3/2)
Force and torque generation in electric machines. AC and DC machines, permanent magnet synchronous (PMSM) and brushless DC motors (BLDC). Machine characteristics and dynamic models of electric actuators. Linear actuators; power electronics device characteristics; motor drives: H-bridges, inverters; speed control methods; power converters.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
MCTR 360
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Spring/Summer,
2-0-3)
A project-based course dealing with the design and implementation of a robotic system to accomplish a set of requirements. Integration of sensor technologies, sensor data processing, motion control based on feedback and real-time programming. Design procedures, ethics, safety and risk management, theory of engineering design, role of engineering analysis in design, application of computer-aided design software; component and material selection, codes, and standards; design optimization; system integration and verification through testing; teamwork, and a design project. Corequisite: MCTR 365.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 28.3 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 56.7 Units
MCTR 365
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(Spring/Summer,
2-0-3)
Mechatronic and robotic system design using CAD tools. Concepts of function structure models, material selection, and introduction of load and stress analysis. Integration of sensors and actuators. Simulation of mechanisms, dynamics, kinematics, and heat transfer using commercial software. Emphasis is on numerical model design including testing and verification methods, and the critical interpretation of the computed results. Design project aligned with MCTR 360.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.0 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
MCTR 370
★ 3.0
(fi 6.0)(Spring/Summer,
3-0-0)
Fundamentals of machine learning methods. Supervised, unsupervised, and reinforcement learning concepts, and fundamentals of fuzzy logic. Review of probability and optimization. Linear regression. Linear classification and logistic regression. Components of modern machine learning approaches, including feature engineering, neural network models, training and evaluation methodology, and deep learning libraries. Object detection and object/human pose regression for robotic applications. Bias in machine learning algorithms. Corequisite: MCTR 399.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.8 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 399
★ 3.0
(fi 6.0)(Spring/Summer,
3-0-0)
Analytical and numerical methods with mechatronics applications. Complex numbers, partial differential equations, analytic functions, elementary functions, mappings, integrals, series, residues and poles, integral formulas. Statistical tests. Numerical integration and differentiation, solution methods of boundary value problems. Use of programming languages to implement numerical methods. Critical-thinking applied to problems related to mechatronics systems. Formulation, methodologies, and techniques for numerical solutions of engineering issues, particularly those arising within the field of mechatronics.
Accreditation Units
Math and Natural Sciences: 44.1 Units
Fall Term 7
Complementary Elective
A complementary elective of the student's choice. Please consult the calendar for more information.
ENG M 401
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-0)
The application of the fundamentals of engineering economics, financial analysis and market assessment to engineering alternatives in the planning, development and ongoing management of industrial enterprises. The course covers the use of engineering, economic, financial and market assessment information in investment and business operation decisions in technology oriented companies. Note: Credit cannot be obtained for more than one of ENGG 310, ENGG 401, ENG M 310, or ENG M 401.
Accreditation Units
Program/Technical Elective
A program/technical elective of the student's choice. Please consult the calendar for more information.
Program/Technical Elective
A program/technical elective of the student's choice. Please consult the calendar for more information.
MCTR 420
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Fall term,
3-0-3/2)
System states and state space models. Linearization of nonlinear state-space models. Solving linear time-invariant state-space equations. Controllability and observability, and their algebraic tests. Minimal state-space realizations. State feedback and eigenvalue/pole assignment. Step tracking control design. State estimation and observer design. Observer-based control. Introduction to linear quadratic optimal control. Prerequisite: MCTR 320.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 460
★ 2.5
(fi 6.0)(Fall term,
1-0-3)
PART 1: Feasibility study and detailed design of a project which requires students to exercise creative ability, to make assumptions and decisions based on synthesis of technical knowledge, and devise new designs. Advanced design safety review.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 56.7 Units
Winter Term 8
ITS Elective
An ITS elective of the student's choice. Please consult the calendar for more information.
ENGG 400
★ 1.0
(fi 2)(either term,
1-0-0)
The technical and professional duties and responsibilities of the engineer; the ethics of the engineering profession; technical and professional organizations. The role of the engineer in the social environment including elements of equity, concepts of sustainable development and environmental stewardship, public and worker safety and health considerations including the context of the Alberta Occupational Health and Safety Act. Note: Restricted to fourth-year traditional and fifth-year co-op engineering students. Must be taken in last term of program.
Accreditation Units
MCTR 421
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Review of probability, random variables, and stochastic processes. Recursive state estimation: Bayes filter, linear Kalman filter and its extension to nonlinear systems. Practical applications of filtering techniques to mechatronics systems. Prerequisite: MCTR 420.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 11.8 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
MCTR 461
★ 2.5
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
1-0-3)
PART 2: Feasibility study and detailed design of a project which requires students to exercise creative ability, to make assumptions and decisions based on synthesis of technical knowledge, and devise new designs. Advanced design safety review. Prerequisite: MCTR 460.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 56.7 Units
MCTR 465
★ 3.8
(fi 6.0)(Winter term,
3-0-3/2)
Introduction to mobile robots. Means of locomotion and kinematic and dynamic models. Linear and nonlinear motion control theory and filtering applied mobile robots. Map-based and reactive motion planning. Localization and mapping. Visual servoing. Prerequisite: MCTR 394. Corequisite: MCTR 421.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 35.4 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
Program/Technical Elective
A program/technical elective of the student's choice. Please consult the calendar for more information.
Space
Electives_1
BME 513
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(second term,
3-0-0)
Introduction to basic physical and technological aspects of medical imaging. Emphasis on computed transmission and emission tomography, magnetic resonance, and ultrasound imaging. These methods are developed and contrasted in terms of how imaging information is generated, detected, and processed and how different hardware configurations and other factors limit image quality. Relative diagnostic potential of the imaging methods is also discussed in relation to future prospects of each method.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 37.8 Units
BME 553
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(second term,
3-1s-0)
Introduction to rehabilitation techniques for assisting individuals with physical disabilities to reach, stand and walk. Biomechanics of intact and pathological movements and the use of assistive devices such as exoskeletal orthotics, neuroprosthetic devices and locomotor training are emphasized. Students are exposed to the concepts of biomechanical modeling, motion analysis, electrical stimulation, control systems, neuroregeneration, and pharmacology. Prerequisite: BME 320 and BME 320 321 or consent of Instructor.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 22.1 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
CMPUT 428
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-3)
Introduction to the geometry and photometry of the 3D to 2D image formation process for the purpose of computing scene properties from camera images. Computing and analyzing motion in image sequences. Recognition of objects (what) and spatial relationships (where) from images and tracking of these in video sequences. Prerequisites: CMPUT 201 or 275; one of CMPUT 340, 418, ECE 240, or equivalent knowledge; one of MATH 101, 115, 118, 136, 146 or 156, and one of MATH 102, 125, or 127.
Accreditation Units
ECE 405
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(first term,
3-0-0)
Introduction to the principles of biophysical instrumentation. Various sensors are examined including strain gauges, inductive, capacitive, thermal, and piezoelectric sensors. Methods of measuring blood pressure are discussed. Origin of biopotentials; membrane and action potentials. Measurement of bioelectrical signals such as the ECG and EMG. Electrical safety, noise, impedance matching, and analog-to-digital conversion. Applications of electrodes, biochemical sensors, and lasers. Prerequisite: ECE 203 or E E 250 or consent of the Instructor. Credit may be obtained in only one of ECE 405 or EE BE 512.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 9.4 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 37.8 Units
ECE 440
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-3/2)
Extension of sampling theory and the Fourier transform to two dimensions, pixel operations including gray-level modification, algebraic and geometric transformations. The design of spatial filters for noise reduction, image sharpening and edge enhancement, and some discussion of interpolation techniques. An introduction to the concepts of image restoration from known degradations and the reconstruction of images from parallel and fan projections. Prerequisite: ECE 340 or E E 338 or consent of Instructor. Credit may be obtained in only one of EE BE 540 or ECE 440.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 14.2 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
ECE 442
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-3/2)
Human visual/audio perception and multimedia data representations. Basic multimedia processing concepts, multimedia compression and communications. Machine learning tools for multimedia signal processing, including principle component analysis and Gaussian mixture modeling. Applications to human-computer interaction, visual-audio, and visual-text processing. Prerequisites: ECE 220 or CMPUT 275, ECE 342, MATH 102 or equivalent knowledge. Credit may be obtained in only one of ECE 442 or E E 442.
Accreditation Units
ECE 449
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-3/2)
Intelligent systems for automatic control and data analysis. The concepts of vagueness and uncertainty, approximate reasoning, fuzzy rule-based systems and fuzzy control. Strategies for learning and adaptation, supervised and reinforcement learning, self-organization and the selection of neural network architectures. Discussion of the principles of search and optimization, evolution and natural selection and genetic algorithms. Introduction to hybrid intelligence. Applications of intelligent systems for pattern recognition, classification, forecasting, decision support, and control. Credit may be obtained in only one of CMPE 449 or ECE 449.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 23.6 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 47.2 Units
Electives_2
ECE 455
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-0)
Microfluidic and nanobiotechnological devices. Fabrication techniques for devices: self-assembly, lithographic technologies. Applications of nanobiotechnology in computing, electronics, human health, environment and manufacture. Prerequisites: MATH 201 or PHYS 230. Credit may be obtained in only one of ECE 455 or E E 455.
Accreditation Units
ECE 458
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-0)
Overview of microelectromechanical (MEMS) systems, applications of MEMS technology to radio frequency, optical and biomedical devices. Basic MEMS building blocks, cantilever and clamped-clamped beams. Actuation mechanisms of mechanical microdevices, thermal and electrostatic. The thin film fabrication process, deposition, lithography, etching and release. MEMS in circuits, switches, capacitors, and resonators. Prerequisites: ECE 370 or E E 315 or PHYS 381, and one of MAT E 201, PHYS 244, MEC E 250. Credit may be obtained in only one of ECE 458 or E E 458.
Accreditation Units
ECE 464
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-3/2)
Basic concepts of computer-integrated intervention. Surgical CAD/CAM, assist and simulation systems. Actuators and imagers. Medical robot design, control and optimization. Surgeon-robot interface technology. Haptic feedback in surgical simulation and teleoperation. Virtual fixtures. Time delay compensation in telesurgery. Cooperative manipulation control. Overview of existing systems for robot-assisted intervention and for virtual-reality surgical simulation. Prerequisite: ECE 360 or ECE 462 or E E 357 or E E 462 or consent of the Department. Credit may be obtained in only one of ECE 464 or E E 464.
Accreditation Units
ECE 487
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-0)
Network topologies. Layered architectures and the Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) reference model. Peer-to-peer protocols, medium access control protocols, and local area network standards. Packet switched networks and routing, the TCP/IP suite of protocols. Credit may be obtained in only one of ECE 487, CMPUT 313 or CMPE 487.
Accreditation Units
ENG M 514
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-0)
Concepts of reliability, failure rate, maintainability, and availability. Properties of various statistical distributions and their applications in reliability engineering. Failure data analysis techniques including probability plotting. Load and strength interference in mechanical component design. System reliability models and system reliability evaluation methods. Optimal system design considering reliability issues. Prerequisite: STAT 235 or equivalent.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 18.9 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 37.8 Units
ENG M 530
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-0-0)
Introduction to project management tools, techniques, templates, and methodologies. This course examines the eight knowledge areas of the Project Management Institute (PMI) which provide an integrated approach to managing engineering projects. Prerequisites: One of ENGG 310, 401 or ENG M 310, 401.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 37.8 Units
ENG M 558
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-0)
Fundamental methods for the analysis of human systems in industrial engineering. Human-machine interaction. Engineering of the workplace and the work environment. Motion and time study. Standards in ergonomics and work design.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 37.8 Units
Electives_3
ENGG 406
★ 3.8
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-3s/2-0)
Introduction to process safety. Basic concepts of fires, explosions and releases. Introduction to process hazards analysis, methodologies and tools. Overview of process safety management frameworks. Case studies and industrial tour(s) demonstrate the application of specialized tools and methodologies in complex industrial operations across all engineering disciplines. Seminars develop competencies and proficiencies in applying these specialized methodologies and tools towards proactive risk management. Requires payment of additional student instructional support fees Refer to the Tuition and Fees page in the University Regulations section of the Calendar. Prerequisite: ENGG 404 or consent of the instructor.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science: 18.9 Units
Engineering Design: 16.5 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 35.4 Units
MAT E 481
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term,
3-1s-0)
Terminology, welding processes and materials considerations, mechanisms of welding including the welding arc, molten metal issues, mass and energy balances, heat transfer, basics of procedure development, design of weldments, codes and standards, non-destructive testing, guest lectures from industrial practitioners and specialists. Pre-requisites: Completion of 2 years in any engineering discipline or consent by Instructor.
Accreditation Units
MEC E 331
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-0-1)
External flow, boundary layers, momentum theories, similitude, fluid metering, fluid friction, fluid friction in pipes, pipe networks. Prerequisites: MEC E 230, 250, MATH 209. Corequisite: CH E 243. Credit can only be granted for one of MEC E 330 or MEC E 331.
Accreditation Units
MEC E 364
★ 3.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
2-0-3)
Primary manufacturing processes including casting, forming, machining, powdered metallurgy and surface technology, interactions between design, materials (metals, polymers, ceramics, composites) and processes, selected field trips and laboratory activities. Requires payment of additional student instructional support fees. Refer to the Tuition and Fees page in the University Regulations section of the Calendar. Prerequisite: MEC E 260.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 44.1 Units
MEC E 464
★ 4.0
(fi 2)(either term or Spring/Summer,
1-2s-4)
Design of machine components for ease of manufacture. Application of measurement, inspection, and reverse engineering techniques. Preparation of working drawings for manufacturing. Introduction to machining operations, including hands-on machine shop practice. Evaluation of design performance. Sections offered at an increased rate of fee assessment; refer to the Tuition and Fees page in the University Regulations sections of the Calendar. Prerequisites: MEC E 260, 265, 300, and 301.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 50.4 Units
MEC E 485
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-0)
Biomechanics; mechanical characterization of biological tissues using elastic and viscoelastic models. Rheology of blood and flow properties. Static and dynamic analyses of selected physiological systems. Application of biomaterials in external and internal prostheses. Prerequisites: BME 320 and 321; MEC E 300, 362, 380; and MEC E 330 or 331. Credit cannot be obtained in both MEC E 585 and 485.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 37.8 Units
MEC E 537
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-0-0)
Boundary layer flow, vorticity, circulation and aerodynamic lift, wing theory, aeronautical applications. Prerequisite: MEC E 330 or 331.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 37.8 Units
Electives_4
MEC E 539
★ 4.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-0-3)
Model selection and simplification, grid generation and grid independence, transient and advection terms treatment, turbulence modeling, verification and validation, best practices. Hands-on experience with commercial CFD codes to demonstrate the application of: theory, proper setup and analysis. Prerequisites: MEC E 390, and 331 or equivalent.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 56.7 Units
MEC E 563
★ 4.5
(fi 6)(either term or Spring/Summer,
3-0-3)
Application of finite element methods to mechanical engineering problems; topics include direct stiffness methods, assembly, constraints, solution techniques, post-processing, element types and the Galkerin procedure. Applications include beam truss and frame analysis, plane strain and stress problems, heat transfer and dynamic analysis Prerequisites: MATH 300, MEC E 360, 390.
Accreditation Units
Engineering Design: 17.0 Units
Engineering Science and Engineering Design: 56.7 Units
MGTSC 405
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-0)
This course is concerned with methods used to predict the uncertain nature of business trends in an effort to help managers make better decisions and plans. Such efforts often involve the study of historical data and manipulation of these data to search for patterns that can be effectively extrapolated to produce forecasts. This is a business statistics course that covers all aspects of business forecasting where the emphasis is on intuitive concepts and applications. Topics covered include the family of exponential smoothing methods, decomposition methods, dynamic regression methods, Box-Jenkins methods and judgmental forecasting methods (e.g. the Delphi method). Because forecasting is best taught through practice, the course contains numerous real, relevant, business oriented case studies and examples that students can use to practice the application of concepts. Prerequisites: MGTSC 312, MGTSC 352 or OM 352.
Accreditation Units
OM 252
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-0)
A problem-solving course which introduces the student to deterministic and stochastic models which are useful for production planning and operations management in business and government. Note: Students are expected to have basic familiarity with microcomputer applications. Prerequisite: MATH 154 or equivalent and STAT 161 or equivalent. Students may not receive credit for both OM 252 and OM 352.
Accreditation Units
OM 422
★ 3.0
(fi 6)(either term,
3-0-0)
Computer modelling of management systems in such functional areas as accounting, finance, marketing and operations. Basic concepts of deterministic and probabilistic (Monte Carlo) simulation and their applications. Microcomputer implementation of case studies using spreadsheets particularly emphasized. Required term project. Prerequisites: MGTSC 312 (or equivalent STAT course), MGTSC 352 or OM 352; and FIN 301 or ACCTG 311. Not to be taken by students with credit in MGTSC 422.
Accreditation Units
RADDI 514
★ 3.5
(fi 6.0)(,
3-0-0)
The course aims to cover medical image processing and analysis techniques, including de-noising, registration, segmentation, and 3D reconstruction, applicable in diagnostic imaging modalities such as ultrasound, computed tomography (CT), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). The course will also cover machine learning topics related to medical image analysis. Clinical examples in cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, and brain imaging will be discussed. Prerequisite: Linear algebra and knowledge in Python programming language or consent of the Department.
Accreditation Units
