An overview of MATLAB
MATLAB is a commercial "Matrix Laboratory" package which
operates as an interactive programming environment. MATLAB is both a
computer programming language and a software environment.
MATLAB allows you to manage variables, work with different type of data,
perform calculations and generate plots.
MATLAB is a tool
for doing numerical computations with matrices and vectors.
MATLAB has a number of add-on software modules ("toolboxes"), that can
perform specialized calculations.
Starting MATLAB
To start MATLAB double click on the MATLAB icon. This will start the MATLAB
Desktop . From the desktop you can access the Command window
, the Workspace window, the Current directory window,
as well as the Help Browser and other tools.
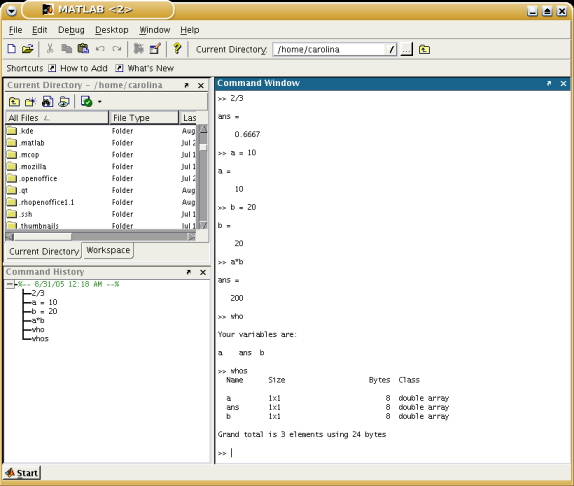
The command window is used to type commands, functions and statements.
Making sure that the cursor is at the prompt of the command window you can
type any command, for example to divide 2 by 3.
MATLAB assigns the answer to a variable called "ans", which is the abbreviation
for answer. The variable "ans" can be used then form further calculations.
MATLAB retains the previous keystrokes in a command file. The up and down
arrow keys can be used to scroll back and forth through the commands.
Workspace
The term workspace refers to the names and values of any variables
in use in the current work session.
Variables
Variable names must
begin with a letter and must contain less than 32 characters. MATLAB
is case sensitive:
"a"
is not the same as "A."
If this proves to be an annoyance, the command
casesen
will toggle the case sensitivity off and on.
The sign "=" (called assignment) is used to assign a value to a variable.
Managing the work session
Some of the commands and symbols to manage the work session are:
|
clc
|
clears the command windows
|
|
clear
|
clears all variables from memory.
|
|
clear var1 var2
|
clears var1 and var2 from memory
|
|
exist('name')
|
determines if a file or variable exists having the name 'name'
|
|
quit
|
stops MATLAB
|
|
who
|
list variables in memory
|
|
whos
|
list variables ans sizes and indicates if they have imaginary
parts
|
|
: colon
|
generates an array having regular spaced elements
|
|
, comma
|
separates elements of an arrays
|
|
; semicolon
|
suppresses screen printing, also denotes a new row in an array
|
|
... Ellipsis
|
continues a line
|
Several commands can be entered in the same line if they are separated by
a comma or semicolon.
Predefined constants
MATLAB has several predefined constants:
Inf 5/0
(Infinity)
eps
(epsilon, specifies the accuracy of the floating point precision)
i
(imaginary number)
ans
(Temporary variable containing the most recent answer)
NaN
(Indicates and undefined numerical result)
pi (Value of pi)
Saving and retrieving your workspace
If you want to stop using MATLAB but continue the session at a
later time, you must use the
save
and
load
commands. Typing
save
causes MATLAB to save the workspace variables, i.e. the variables
name, their sizes and their values in a binary file called
matlab.mat. Only MATLAB can read the
*.mat
files. To retrieve your workspace variable, type
load
Note: it is important to know the locations of the files you use with
MATLAB. File location frequently causes problems. You can display the
contents of the current directory by typing
dir
and the path by typing
path
or by looking at the toolbar as detailed below.
Menus and the toolbar
A menu can be found across the top of the desktop, the group of
icons displayed below it is the toolbar. To the right of the toolbar
a box displays the current directory.
Depending on the actions executed MATLAB will generate other type of windows.
Such is the case when:
- generating plots, MATLAB will open a graphical window.
- editing/debugging a file, MATLAB will open its own editor window.
For each window type MATLAB will change its menu, this means that MATLAB's
menus are context sensitive.
Using MATLAB
You can perform operations in MATLAB in two different ways:
-
Computing
with MATLAB (Interactive mode)
In the interactive mode
all commands are entered directly in the command window.
-
Programming in MATLAB
By running a MATLAB program (script file). The MATLAB file (
*.m) contains MATLAB commands. Running your program is equivalent to
typing all the commands, one at a time, at the command window
prompt. You can run the file by typing its name at the command
window prompt.
References
