Ch E 416 - Assignment 1 Solutions
Question 1
(a)
Using the MATLAB code and thermophysical
properties given with the assignment, fugacity data was obtained and plotted
for propane. Liquid and vapor fugacities are equal
at the saturation point.
(b)
By inspection
of the plot, the saturation temperature appears to be approximately 287.0 K
(= 13.85 0C). This agrees quite well with the literature value
of Tsat = 286.53 K from NIST
database.
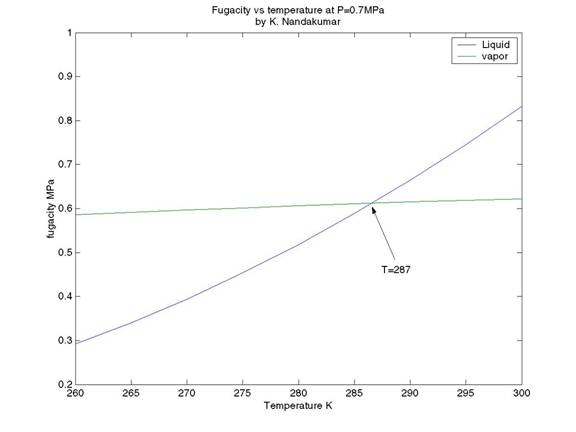
One can also solve precisely for the saturation
temperature by making the fugacities equal in both
the phases. The following function can be used with “fsolve” in MATLAB to solve the problem.
function f=A1_Tb(T,P,Tc,Pc,w)
%to find the value of T that makes
the difference between fg and fl zero
%use MATLAB function fsolve.
%options=optimset('Display','Iter');
%fsolve('A1_Tb',230,options,0.7,369.83,4.245517,0.152291)
[fl,fg]=A1_fugT(T,P,Tc,Pc,w);
f=fl-fg;
end
Here are the results.
options=optimset('Display','Iter');
fsolve('A1_Tb',230,options,0.7,369.83,4.245517,0.152291)
Norm
of First-order
Iteration
Func-count f(x) step optimality CG-iterations
1 3 0.197851 1 0.000999 0
2 5 0.171089 10 0.00166 1
3 7 0.0864436 20 0.00237 1
4 9 0.0228214 36.4924 0.00247 1
5 11 9.09319e-005 9.23661 0.000136 1
6 13 2.62979e-009 0.668027 7.24e-007 1
Optimization terminated successfully:
First-order optimality less than OPTIONS.TolFun, and no negative/zero curvature detected
ans =
286.5878
(c) At
the saturation temperature of
T=286.5878, the compressibilities are obtained as
follows from MATLAB.
[fl,fg,zL,zG]=A1_fugT(286.5878,0.7,369.83,4.245517,0.152291)
fl =
0.6120
fg =
0.6120
zL =
0.0242
zG =
0.8576
> rhoL=0.7/8.314472E-3/zL/286.5878
rhoL =
12.1339 %mol/l
>> rhoG=0.7/8.314472E-3/zG/286.5878
rhoG =
0.3426 %mol/l
%Note from NIST
data base, the values are: (11.558,0.34412) mol/l
(d)
Using the ASPEN
simulator with the RK-ASPEN EOS to calculate pure component properties, the
following graph was generated for the fugacity coefficient PHI. The
saturation temperature appears to be T = 286.5 K.
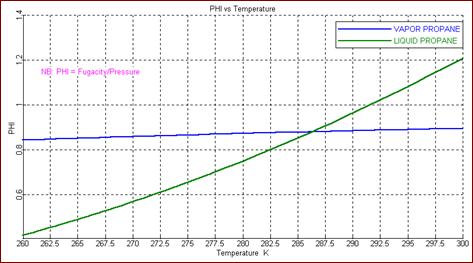
(e) From
the two plots at T = 280 K, the PR-EOS gives fL
= 5.12 bar and fV = 6.05 bar, for
the liquid and vapor phase fugacities,
respectively. The RK-ASPEN EOS gives approximately fL
= 5.25 bar and fV = 6.16 bar.
Question 2
(a)
The previous
MATLAB code was modified to determine fugacities over a range of pressures. Again, the thermophysical properties given at the end of the
assignment were used. Once fugacity data was generated, it was plotted.
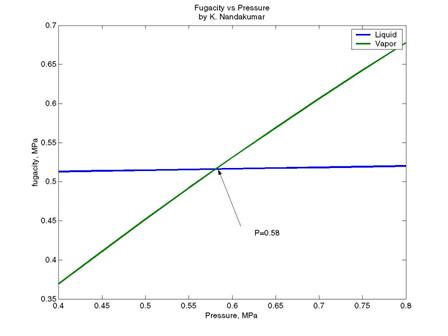
(b) At a given temperature (T=280 K), liquid and vapour fugacities are equal at
the saturation pressure. By inspection of the plot, the saturation pressure
at 280 K appears to be approximately 0.58 MPa.
It can also be computed more precisely using “fsolve”
that makes the fugacities equal by varying the
Pressure. Here is how it works:
function
f=A1_Pv(P,T,Tc,Pc,w)
%to find the value of P that
makes the difference between fg and fl zero
%use MATLAB function fsolve.
%options=optimset('Display','Iter');
%fsolve('A1_Pv',0.5,options,280,369.83,4.245517,0.152291)
[fl,fg]=A1_fugT(T,P,Tc,Pc,w);
f=fl-fg;
Here are the results.
>> fsolve(‘A1_Pv’,0.5,options,280,369.83,4.245517,0.152291)
Norm
of First-order
Iteration
Func-count f(x) step optimality CG-iterations
1 3 0.00393073 1 0.0496 0
2 5 1.41227e-006 0.0792466 0.000905 1
3 7 2.12884e-013 0.0015613 3.51e-007 1
Optimization terminated successfully:
First-order optimality less than OPTIONS.TolFun, and no negative/zero curvature detected
ans =
0.5808 %Sat Press in MPa
From
NIST database, the saturation pressure at T=280 K is P=0.58189 Mpa
very close! Look at the power of equations of state!
Question 3
The binary interaction
parameters (kij's) from HYSYS are (with
methane=1,ethane=2, n-propane=3):
k11 = k22 = k33 = 0
k12 = k21 = 0.00224
k13 = k31 = 0.00683
k32 = k23 = 0.00126
Now, writing the necessary equations as MATLAB code
and using the thermophysical properties given in
the table at the end of the assignment, we find:
T = 224.8168; % K
P = 13.7895; % bar
y = [0.4 0.4 0.2];
Tc = [190.6 305.4
369.8]; % K
Pc = [45.4 48.2 41.9]*1.01325; % bar
w = [0.008 0.099493
0.152291];
k(3,3)=0; %
interaction of species with itself
k(1,2)=2.24e-003;
k(2,1)=k(1,2);
k(2,3)=1.26e-003;
k(3,2)=k(2,3);
k(1,3)=6.83e-003;
k(3,1)=k(1,3);
fugV = A1_fug_mix(T,P,y,Tc,Pc,w,k)
fugV =
5.3957 4.2073 1.7033
===============NOTE=================
*** These values are expressed in bar ***
Question 4
The binary interaction
parameter is obtained from HYSYS. k1,2=0.00258
Experimental values of equilibrium ratios:
K1=y1/x1=0.6650/0.2900=2.293
K2=y2/x2=(1-0.6650)/(1-0.2900)=0.3350/0.7100=0.472
a12=K1/K2=2.293/0.472=4.86
From Raoult’s law:
K1=P1s/P=409.6/147=2.786
K2=P2s/P=58.6/147=0.399
a12=K1/K2=2.786/0.399=6.98
K-values from an EOS:
FL,1(T,P,x1,x2)=
FV,1(T,P,y1,y2)
FL,2(T,P,x1,x2)= FV,2(T,P,y1,y2)
x1+x2=1
y1+y2=1
Given (T=167 oF,
P=147 psia), solve the above four equations given
in the function A1_Kval_PR for the unknowns using fsolve. The script file used is A1_P4.m.
The results are given below:
options=optimset('TolFun',1e-6,'Display','Final');
xx=fsolve('A1_Kval_PR',[.29 .71 0.665
0.335],options);
x = xx(1:2)
y = xx(3:4)
K = y./x
alpha_12 = K(1)/K(2)
Optimization terminated:
first-order optimality is less than options.TolFun.
x =
0.29066 0.70934
y =
0.66025 0.33975
K =
2.2715 0.47897
alpha_12 =
4.7425
a12=K1/K2= 4.7425 (Compares well with the experimental value
of 4.86)
Notes:
(1) The code given is based on temperatures in K and pressures in bar (not
atm). To use this code you needed to enter all thermophysical property data in the correct units.
(2)Fugacity has the same units as pressure!
Posted Sept 22, 2006
Return
to Assignments Page
|


